Leucines
The leucines are primarily the four isomeric amino acids: leucine, isoleucine, tert-leucine (terleucine, pseudoleucine) and norleucine. Being compared with the four butanols, they could be classified as butyl-substituted glycines; they represent all four possible variations.
Leucine and isoleucine belong to the proteinogenic amino acids; the others are non-natural.
Isomers
Including the stereoisomers, six further isomers could be added: D-leucine, D-isoleucine, L-alloisoleucine, D-alloisoleucine, D-tert-leucine and D-norleucine.
| Leucines | ||||
| Name | L-Leucine | L-Isoleucine | L-tert-Leucine (terleucine, pseudoleucine) | L-Norleucine |
| Other names | 2-Amino-4-methylpentanoic acid, Isobutylglycine |
2-Amino-3-methylpentanoic acid, sec-Butylglycine |
2-Amino-3,3-dimethylbutanoic acid, tert-Butylglycine |
2-Amino-hexanoic acid, n-Butylglycine |
| Structure | 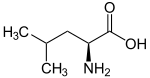 | 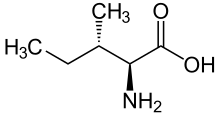 | 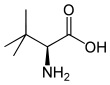 | 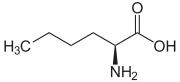 |
| CAS-number | 61-90-5 | 73-32-5 | 20859-02-3 | 327-57-1 |
| PubChem | CID 6106 from PubChem | CID 791 from PubChem | CID 164608 from PubChem | CID 21236 from PubChem |
| Molecular formula | C6H13NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 131.18 g/mol | |||
Derivatives
Cycloleucine could be classified as a cyclic derivative of norleucine. With a cyclopentane-ring, it has two hydrogen atoms fewer and thus is not an isomer. The α-carbon atom is not a stereocenter.
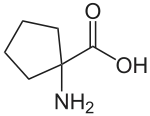
Cycloleucine
See also
Literature
- Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer: Biochemie. 6 Auflage, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2007. ISBN 978-3-8274-1800-5.
- Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet: Biochemistry. 3. Auflage, John Wiley & Sons, New York 2004. ISBN 0-471-19350-X.
- Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Peter Walter, Julian Lewis, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts: Molecular Biology of the Cell, 5. Auflage, Taylor & Francis 2007, ISBN 978-0815341062.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.