List of the oldest buildings in Connecticut
This article lists the oldest extant buildings in the state of Connecticut in the United States of America, including houses and any other surviving structures. The dates of construction are approximate and based on land tax and probate records, architectural studies, genealogy and dendrochronology. All entries should include a citation with reference to support the date of construction. Buildings on the list should be limited to the First Period of American architecture. If the exact year of construction is estimated, it will be shown as a range of dates. The location shown is the original township where the building was constructed.
| Building | Image | Township | Built | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henry Whitfield House |  |
Guilford | 1640 | Oldest surviving stone American Colonial house in New England, museum since 1899.[1] |
| Feake-Ferris House | Greenwich | 1645 | The age of the structure was verified by Columbia University dendrochronologists at the Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory[2] conducting "[a] 2015 dendrochronology analysis of the house [which] dated the west side of the existing house--the Feake House--to 1645; the north "lean-to" addition to the Feake house made by Jeffrey Ferris to 1660; and the east side and expansion of the "lean-to" - the James Ferris expansion - to 1689."[3][4] | |
| John Hollister House |  |
Glastonbury | 1649-1675 | Has hewn overhang with supporting corbels. |
| Thomas Lee House | .jpg.webp) |
East Lyme | 1660–1664 | Began as a one-room house, oldest wooden saltbox still in its primitive state, museum since 1897.[5] |
| Deacon John Moore House |  |
Windsor | 1664 | Moore was also a woodworker known for using the foliated vine design, which depicts vines and blossoms carved in shallow relief with flat surfaces. |
| Dr. Philip Turner House | .jpg.webp) |
Norwich | 1670 | Believed to have been originally built in 1670, the house was later occupied by American Revolutionary surgeon Philip Turner. |
| Elisha Bushnell House |  |
Old Saybrook | 1678 | The Colonial property includes two contributing buildings, the second being termed the "Slave House". |
| Joshua Hempsted House |  |
New London | 1678 | One of the earliest documented houses in Connecticut, now a museum.[6] |
| Thomas Wheeler House |  |
Bridgeport | 1680-1720[7] | Was once part of Fairfield and is an area with deep colonial maritime history. |
| Deacon John Graves House |  |
Guilford | 1681 | Saltbox saved from demolition and fully restored in 1983 by a private foundation, now a museum in Madison.[8] |
| Ephraim Hawley House |  |
Stratford | 1683-1690 | 1 1⁄2-story Cape Cod cottage saltbox, hand-riven oak clapboard in situ in lean-to attic. |
| Acadian House |  |
Guilford | 1690 | Saltbox named after the Acadians who lived there following 1755 deportation from Canada.[9] |
| John Randall House |  |
Stonington | 1690 | Notable for its restoration in the 1930s by early preservationist Norman Isham. |
| Meigs-Bishop House |  |
Guilford | 1690 | English tea room in Madison.[10] |
| John Whittlesey Jr. House |  |
Old Saybrook | 1693 | Private residence listed on the NRHP. |
| Comfort Starr House |  |
Guilford | 1695 | Original oak clapboard in lean-to attic, residence.[11] Dendrochronology in 2014 confirmed a construction date of 1695.[12] |
| General David Humphreys House | 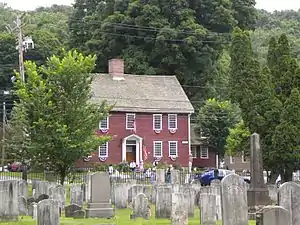 |
Ansonia | 1695–1698 | Home of the first U.S. Ambassador, now a museum. |
| Avery Homestead |  |
Ledyard | 1696 | Begun as a single-story, one-room house and later expanded to a two-story, two-room house by 1726. |
| Hoyt-Barnum House |  |
Stamford | 1699 | Early Cape Cod Cottage, Stamford Historical Society museum.[13] |
| Eells-Stow House |  |
Milford | 1700–1720 | Served as a hospital during Revolutionary War, now a museum.[14] |
| Pond-Weed House |  |
Darien | 1700 | Saltbox residence. |
| Samuel Huntington Birthplace |  |
Scotland | 1700–1722 | Saltbox home of a signer of the Declaration of Independence and Governor of Connecticut, now a museum.[15] |
| Stanton-Davis Homestead Museum |  |
Stonington | 1700[16] | A working farm for the last 340 years. |
| Stanley-Whitman House | .jpg.webp) |
Farmington | 1709–1720 | Saltbox with framed overhang style with carved pendants, now a museum.[17] |
| John Tyler House |  |
Branford | 1710 | Private residence listed on the NRHP. |
| Buttolph-Williams House |  |
Wethersfield | 1711 | Connecticut Landmark museum.[18] |
| Black Horse Tavern (Old Saybrook, Connecticut) |  |
Old Saybrook | 1712 | Private residence listed on the NRHP.[19][20] |
| Hyland House |  |
Guilford | 1713 | Saltbox with framed overhang and flat plaster ceilings, now a museum.[21] Dendrochronology in 2014 confirmed a 1713 construction date.[22] |
| Captain David Judson House |  |
Stratford | 1723[23] | Georgian architecture with stone foundation and chimney of original stone house built in 1639. |
| Jonathan Whaples House |  |
Newington | 1723 | Built by John Whaples For Jonathan Whaples in 1723 this home is one of the oldest in Newington.[24] |
| Swain-Harrison House |  |
Branford | 1724 | Saltbox with overhang serves as the Branford Historical Society museum.[25] |
| Nehemiah Royce House |  |
Wallingford | 1734 | Saltbox, General George Washington slept here in 1775, once a residence for Choate Rosemary Hall.[26] |
| Thomas Lyon House |  |
Greenwich | 1739[27] | Oldest unaltered saltbox house in Greenwich. |
Notes
- Historic Houses of Early America, Elsie Lathrop, Kessinger, New York, 2006 page 305
- Cook, Edward R.; William J. Callahan, Jr. "A Dendrochronological Analysis of the "Voorhees Family Barn", Branchburg, Somerset County, New Jersey," (September 2016) p.8.
- "The Feake-Ferris House". Greenwich Point Conservancy. Retrieved 2019-10-30.
- "Citation for Feake-Ferris House".
- East Lyme Historical Society website retrieved on 2009-05-11
- Connecticut Landmarks website retrieved on 2009-05-12 Archived 2008-12-08 at the Wayback Machine
- "Wheeler House, Bridgeport".
- Deacon John Graves Foundation website retrieved on 2009-05-17
- Acadians-Guilford Albert Lafreniere website retrieved on 2009-05-13 website
- Front Parlour website retrieved on 2009-05-13 Archived 2009-02-07 at the Wayback Machine
- Connecticut: A Guide to its Roads, Lore and People, Federal WPA Project, 1938 page 165
- Stamford Historical Society website retrieved on 2009-05-12
- Milford Historical website retrieved on 2009-05-12 Archived 2009-10-09 at the Wayback Machine
- Samuel Huntington Birthplace website retrieved on 2009-05-11
- "Stanton-Davis House".
- Stanley-Whitman Museum website retrieved on 2009-05-11
- CT Landmarks website retrieved on 2009-05-11
- NRHP Inventory-Nomination: Black Horse Tavern
- Accompanying 10 photos, exterior and interior, from 1978
- Hyland House Museum website retrieved 2009-05-11
- Orcutt, Samuel (1886). A history of the old town of Stratford and the city of Bridgeport, Connecticut. 1. New Haven, Connecticut: Tuttle, Morehouse & Taylor. p. 89.
- "Home Of Whaples, John, 944 Main St". Treasures of Connecticut Libraries. Retrieved 2019-05-07.
- "Branford Historical Society website retrieved 2009-05-11". Archived from the original on 2008-12-24. Retrieved 2009-05-11.
- "Wallingford Historical Society website retrieved on 2009-05-11". Archived from the original on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2009-05-11.
- "Dendrochronology results in "Architectural Fabric of the Thomas Lyon House Phase 2"".
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.