Malonic anhydride
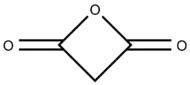
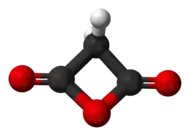
Malonic anhydride or oxetane-2,4-dione is an organic compound with chemical formula C3H2O3 or CH2(CO)2O. It can be viewed as the anhydride of malonic acid, or a double ketone of oxetane.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Oxetane-2,4-dione | |
| Other names
Malonic anhydride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 86.046 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Malonic anhydride was first synthesized in 1988 by ozonolysis of diketene.[1][2] Some derivatives, such as 3,3-dimethyl-oxetane-2,4-dione, are known.[3][4][5]
References
- Cotton, F. A.; Wilkinson, G. (1988) Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 5th edn. Wiley
- H. Mark Perks and Joel F. Liebman (2000). "Paradigms and Paradoxes: Aspects of the Energetics of Carboxylic Acids and Their Anhydrides". Structural Chemistry. 11 (4): 265269. doi:10.1023/A:1009270411806. ISSN 1040-0400.
- Charles L. Perrin; Arrhenius, T (1978). J. Am. Chem. SOC. volume 100, pages 5249-5251.
- Ribeiro da Silva, M. A. J.; Monte, M. J. S.; Ribeiro, J. R.(1999) J. Chem.Thermodyn. 31, 1093.
- Charles L. Perrin, Douglas Magde, Sylvia J. Berens, Julie Roque (1980), Raman spectrum of a malonic anhydride. (Actually, of 3,3-dimethyl-oxetane-2,4-dione.) J. Org. Chem., volume 45 issue 9, pp 1705–1706. doi:10.1021/jo01297a044.
See also
- Carbon suboxide (C3O2), an anhydride of malonic anhydride.
- 2-oxetanone, also called β-propiolactone
- 3-oxetanone
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.