Manú River
The Manú is a river in southeastern Peru. It runs down the eastern slopes of the Andes Mountains into the Amazon Basin. It runs through what is now protected as the Manú National Park, a vast Biosphere Reserve, home to arguably the highest concentration of biodiversity on Earth. Few people live along its length. Much of the park is off-limits to all but permitted scientists and the indigenous groups of Amazonian Indians, mostly of the Machiguenga tribe.
| Manú River | |
|---|---|
 View of riverbank in Manú National Park | |
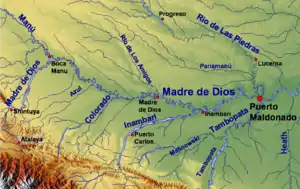 The Madre de Dios watershed with Manú River in the northwest | |
| Location | |
| Country | Peru |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Andes |
| Mouth | Madre de Dios River |
| Length | 300 km (190 mi)[1] |
The Manú is a tributary to the Madre de Dios River, which downriver joins the Madeira River, and ultimately the Amazon River. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, this area of what was organized as the Madre de Dios region was exploited for the production of rubber during the rubber boom, with workers brought in by Brazilian, Bolivian and Peruvian interests.
References
- Ziesler, R.; Ardizzone, G.D. (1979). "Amazon River System". The Inland waters of Latin America. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. ISBN 92-5-000780-9. Archived from the original on 21 October 2013.