Mangalore City Corporation
The Mangalore City Corporation is the municipal corporation responsible for looking after the city administration of the Indian city of Mangalore, the second major city of Karnataka. It consists of a legislative and an executive body. The legislative body is headed by the city mayor while the executive body is headed by a Chief Commissioner.
 | |
 Logo of the Mangalore City Corporation | |
| Formation | 1865 |
|---|---|
| Type | Municipal Corporation |
| Headquarters | Mangalore |
Official language | Kannada, English |
| Diwakara (BJP)[1] | |
| Website | Official website |
History
The council started its functions with 7 members who were then district officers. Most of them were Europeans. The Vice-President was the administrative officer. The income of the municipality was about Rs. 15,000. The population and the area of the town in the year 1866 were about 28,000 and one square mile respectively. In the year 1871, the population of the town was 29,712; and there were 6,619 houses out of which 4,341 were attached. A dispensary was started for the first time in 1868 at the site of the Lady Goschen Hospital. Subsequently a series of legislations under the Madras Presidency resulted in the gradual empowerment of the local administration and facilitated many welfare activities.
Following the re-organization of States, the Mysore Municipalities Act 1964 came into force as a uniform act throughout the state on 1 April 1965, replacing the Madras District Municipalities Act of 1920. The provisions of this act gave a new phase to the municipality and it became a city Municipality. Ample opportunities were made in the Act to raise the income and also to carry out some of the obligatory functions.

Mangalore City Corporation (MCC) came into existence during 3 July 1980,[2] which was formerly a Municipality and was expanded during 1996–97 by including Surathkal Town Municipality, Katipalla Notified area, Panamboor, Baikampady, Kulai, Hosabettu villages. Further during April 2002, it was further extended to include Bajal, Kannuru, Kudupu and Thiruvail Panchayath limits into Mangalore City Corporation.
Mangalore City Corporation presided by a mayor. Mangalore City Corporation currently has a population of more than 600,000 and area of 170 km2 and there is proposal to increase that to 304 km2 by including Mulky in the north and Ullal in the south. It is divided into 60 wards, each represented by a corporator. Elections to the corporation are held every five years and subsequently a mayor and a deputy mayor are elected for a term of one year. It comes under portion of two Lokasabha Constituencies, four Legislative assembly constituencies and one legislative council constituency.
The city corporation is now housed in its own premises located at M. G. Road, Lalbagh, Mangalore. Since its up-gradation as a city corporation, the civic body has spearheaded several developmental activities in the city and it has been adjudged as one of the best corporations in the state for 3 years continuously.
Mangalore City Corporation (MCC) belongs to Mangalore City South and Mangalore City North constituencies in Karnataka Legislative Assembly and Dakshina Kannada - Lok Sabha constituency.
Corporation Elections 2019[3]
| S.No. | Party Name | Party Symbol | Number of Corporators |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | BJP | 44 | |
| 02 | INC | 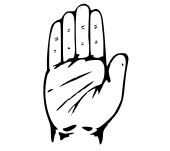 |
14 |
| 03 | SDPI | 2 |
Wards under the MCC
There are 60 wards administered by the Mangalore City Corporation.[4] They are
- Surathkal (West)
- Surathkal (East)
- Katipalla (East)
- Katipalla-Krishnapura
- Katipalla (North)
- Iddya (East)
- Iddya (West)
- Hosabettu
- Kulai
- Baikampady
- Panambur
- Panjimogaru
- Kunjathbail (North)
- Marakada
- Kunjathbail (South)
- Bangrakulur
- Derebail (North)
- Kavoor
- Pachanady
- Tiruvail
- Padavu (West)
- Kadri Padavu
- Derebail (East)
- Derebail (South)
- Derebail (West)
- Derebail (South-west)
- Boloor
- Mannagudda
- Kambla
- Kodialbail
- Bejai
- Kadri (North)
- Kadri (South)
- Shivabagh
- Padavu (Central)
- Padavu (East)
- Maroli
- Bendoor
- Falnir
- Court
- Central Market
- Dongerkery
- Kudroli
- Bunder
- Port
- Cantonment
- Milagres
- Kankanady-Valencia
- Kankanady
- Alape (South)
- Alape (North)
- Kannur
- Bajal
- Jeppinamogaru
- Attavar
- Mangaladevi
- Hoige Bazaar
- Bolar
- Jeppu
- Bengre
References
- "Diwakara from BJP elected Mayor of Mangaluru". The Hindu. 28 February 2020. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- "Smart City project to restore Century-old Mangaluru municipality building". The Times of India. 6 February 2018. Retrieved 28 December 2019.
- "Mangaluru Corporation polls: BJP wins 44 seats, Cong 14". Deccan Herald. 14 November 2019. Retrieved 11 May 2020.
- "Bharatiya Janata Party released 60 wards final list for Mangalore City Corporation election". Megamedia News.