Menthofuran
Menthofuran is an organic compound found in a variety of essential oils including that of pennyroyal (Mentha pulegium). It is highly toxic and believed to be the primary toxin in pennyroyal responsible for its potentially fatal effects.[1] After ingestion of menthofuran, it is metabolically activated to chemically reactive intermediates that are hepatotoxic.[2]
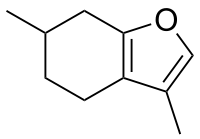 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3,6-Dimethyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzofuran | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.087 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14O | |
| Molar mass | 150.221 g·mol−1 |
| Boiling point | 208 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 86 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Biosynthesis
Menthofuran is produced biosynthetically from pulegone by the enzyme menthofuran synthase.
-menthofuran_synthase_reaction.PNG.webp) Menthofuran synthase converts pulegone to menthofuran
Menthofuran synthase converts pulegone to menthofuran
Synthesis
Menthofuran can be synthesized from 5-methylcyclohexane-1,3-dione and allenyldimethylsulfonium bromide in two steps via a furannulation strategy consisting of enolate addition and rearrangement.[3]
References
- Anderson IB, Mullen WH, Meeker JE, Khojasteh-BakhtSC, Oishi S, Nelson SD, Blanc PD (April 1996). "Pennyroyal toxicity: measurement of toxic metabolite levels in two cases and review of the literature". Annals of Internal Medicine. 124 (8): 726–34. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-124-8-199604150-00004. PMID 8633832.
- Thomassen D, Knebel N, Slattery JT, McClanahan RH, Nelson SD (1992). "Reactive intermediates in the oxidation of menthofuran by cytochromes P-450". Chemical Research in Toxicology. 5 (1): 123–30. doi:10.1021/tx00025a021. PMID 1581528.
- Mariko Aso; Sakamoto, Mizue; Urakawa, Narumi; Kanematsu, Ken (1990). "Furannulation strategy. An efficient synthesis of fused 3-methylfurans". Heterocycles. 31 (6): 1003–6. doi:10.3987/com-90-5392.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.