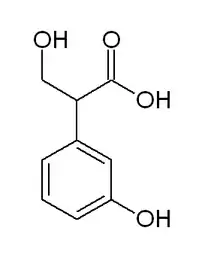
meta-Hydroxyphenylhydracrylic acid
meta-Hydroxyphenylhydracrylic acid is a metabolite in the degradation of (+)-catechin in the crab-eating macaque (Macaca irus) excreted in the urine.[1] It is also a substance found in human urine.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
(-)-β-m-Hydroxyphenyl-hydracrylic acid m-HPHA | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 182.175 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- N. P. Das (1974). "Studies on flavonoid metabolism: Excretion of m-Hydroxyphenylhydracrylic Acid from (+)-Catechin in the Monkey (Macaca iris sp.)". Drug Metab Dispos. 2 (3): 209–213. PMID 4153081.
- Marvin D. Armstrong and Kenneth N. F. Shaw (1956). "The occurrence of (-)-β-m-hydroxyphenyl-hydracrylic acid in human urine". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 225 (1): 269–78. PMID 13416236.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.