Methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphine
Methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphine is a Wittig reagent used as a reagent in the homologization of aldehydes and ketones to extended aldehydes, an organic reaction first reported in 1958 . This reagent is quite unstable to even mild temperatures and water. As such it must be made in situ, taking on a blood red color, indicative of destabilized ylides.
Preparation
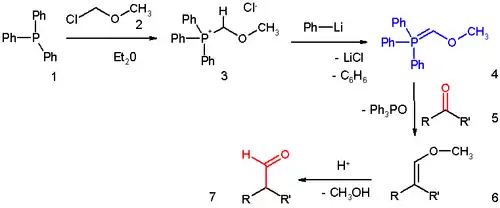
The reagent can be prepared (scheme 1) by reaction of triphenylphosphine 1 with chloromethyl methyl ether 2 in diethyl ether to the phosphonium salt 3. 3 can also be prepared from triphenylphosphine, methylal and acetyl chloride, a reaction avoiding the costly and carcinogenic chloroalkyl ether and especially useful for large batches.
This salt is deprotonated to the phosphonium ylide Methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphine 4 by phenyllithium.
Uses
This reagent reacts with a ketone or aldehyde 5 in a Wittig reaction to the enol ether 6, which can be converted to the aldehyde 7 by the application of an acid.
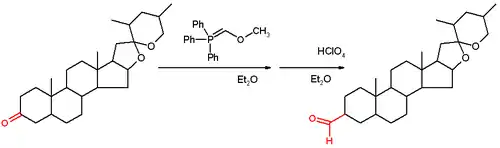
The reaction has been applied to the steroid tigogenone (scheme 2) and in the Wender Taxol total synthesis and in the Stork quinine total synthesis.