Musée du Pays Châtillonnais
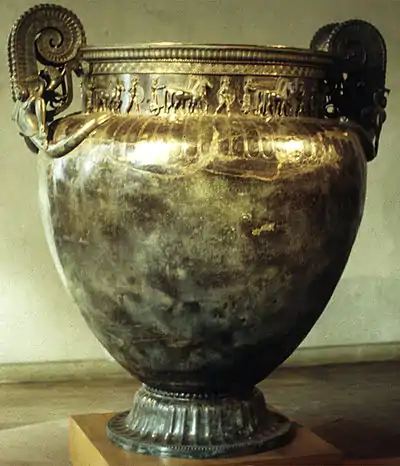
The Musée du Pays Châtillonnais, or Trésor de Vix, formerly called the musée archéologique de Châtillon-sur-Seine (Côte-d'Or), was created in the late nineteenth century and is managed by the community of communes of the Pays Châtillonnais. The museum houses the finding of the Vix Grave, and especially the famous Vix krater, dated to circa 500 BCE and testifying to the links between the Gauls and the Greeks at that period.[1]
 Location in France | |
| Established | 1882 |
|---|---|
| Location | Notre-Dame de Châtillon, Châtillon-sur-Seine |
| Coordinates | 47.863732°N 4.575181°E |
| Collection size | Prehistory and history |
| Website | www |

History

Throughout France the second half of the nineteenth century was an era of growing interest in archeology. The subject was particularly popular in the Côte-d'Or region since major excavations had been organized by Napoleon III on the site of Alesia, 80 kilometres (50 mi) from Châtillon. In 1882 the Châtillon Archaeological and Historical Society opened the first museum, to be a museum of archaeology. The region is rich in archaeological relics. The excavations of the Gallo-Roman Vertillum, about fifteen miles away, and those of Mount Lassois, produced a large number of objects.
In 1928 the society acquired a Renaissance hotel downtown, the hotel Philandrier, named after William Philandrier, an architect born in Chatillon in the 16th century. In 1950 the museum expanded with a move into the hotel, which provided an exhibition area of 400 square metres (4,300 sq ft). Three years later the discovery of the Vix Grave, a burial of prime importance for its richness and historical interest, brought international recognition to the museum. It was able to collect all the treasures of the site, which otherwise would probably have been taken to the National Archaeological Museum at Saint-Germain-en-Laye.
In 2009, the museum left the hotel Philandrier, which had become too cramped, and moved to the old abbey of Notre-Dame de Châtillon. Founded in the 12th century by Bernard of Clairvaux and rebuilt in the 17th and 18th centuries, the chateau had until recently been a hospital and nursing home. The design of the new museum was assigned to the architect Antoine Stinco. The new museum site has 2,000 square metres (22,000 sq ft) in a prestigious setting.[2] Taking advantage of the move, the museum reorganized its collection, which now covers the entire prehistory and history of the region up to the 18th century.
Collections
- Prehistory: Numerous chance finds, excavations of mount Lassois Mount and the Cave of La Grande Baume at Balot.
- Early History: The graves of Sainte-Colombe-sur-Seine, the Treasure of Vix with the famous Cratère de Vix. Deposits from the source of Douix.
- The Gallo-Roman world: The city of Vertillum, the sanctuary of Essarois and the sanctuary of Tremblois at Villiers-le-Duc.
- The Middle Ages: The Art of Fontenay Abbey and the Abbey of Notre-Dame de Châtillon, the relics of St. Vorles.
- From the Renaissance to the eighteenth century through many objects of daily life, business and the metal industry.
- Marshal Marmont, a native of Chatillon, for whom there is a memory room.
The museum opened its doors to the new site on 4 July 2009. There are experiments in the DIVINE system, a visitor assistance program with interactive multimedia content delivered by Wi-Fi.[3]
References
- Claude Orrieux. A history of ancient Greece. p. 62.
- "Communiqué de presse - Janvier 2009" (PDF). Châtillonnais. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-08-14. Retrieved 2012-05-17.
- "DIVINE2, visitez autrement". Tresor de Vix. Retrieved 2012-05-17.
External links
- "Official website". Musée du Pays Châtillonnais.