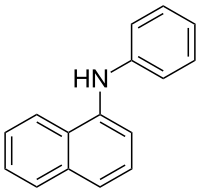
N-Phenylnaphthalen-1-amine
N-Phenylnaphthalen-1-amine (NPN) is a nonpolar, hydrophobic molecule with the chemical formula C
16NH
13. This molecule is most notable for its binding affinity in mouse major urinary protein (MUP). This ligand has the greatest binding affinity of all MUP binding ligand discovered, including 2-sec-butyl-4,5-dihydrothiazole (SBT), 6-hydroxy-6-methyl-3-heptanone (HMH), and 3-isobutyl-2-methoxypyrazine (IBMP). NPN binds 28 times tighter than SBT. It also makes 38 nonpolar contacts to MUP, whereas IBMP only makes 15 contacts which are the next most nonpolar contacts.[1] There is a slight difference in the binding affinities and forms for NPN bound in wild-type MUP and the Y120F MUP mutant. In wild-type MUP there is just enough room for the amine group of NPN to makes a water mediated hydrogen bond to Tyr120, whereas in Y120F MUP mutant, there is a slight shift and the amine group makes a direct hydrogen bond to Tyr120. Much is still unknown about the entropic and enthalpic effects of the MUP binding site.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-Phenylnaphthalen-1-amine; α-Naphthylphenylamine | |
| Other names
anilinonaphthalene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | PANa |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.803 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H13N | |
| Molar mass | 219.287 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Pertinhez TA, Ferrari E, Casali E, Patel JA, Spisni A, Smith LJ (1 December 2009). "The binding cavity of mouse major urinary protein is optimised for a variety of ligand binding modes". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 390 (4): 1266–1271. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.133. PMID 19878650.
- Homans, SW (July 2007). "Water, water everywhere--except where it matters?". Drug Discovery Today. 12 (13–14): 534–9. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2007.05.004. PMID 17631247.