National Institutes of Natural Sciences, Japan
The National Institute of Natural Sciences (自然科学研究機構, Shizenkagaku kenkyuukikou) (NINS) is an inter-university research institute corporation consisting of five member institutes: the National Astronomical Observatory (NAOJ), the National Institute for fusion Science (NIFS), the National Institute for Basic Biology (NIBB), the National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS), and the Institutes for Molecular Sciences (IMS). NINS was established in April 2004 to bring about further development of the natural sciences in Japan.[1]
| Established | 2004 |
|---|---|
| President | Akio Komori |
| Staff | 888 |
| Budget | 43 Billion yen in total |
| Address | Kamiyacho Central Place 2F 4-3-13 Toranomon, Minato-ku Tokyo, 105-0001 Japan |
| Location | |
| Website | http://www.nins.jp/english |
Outline
NINS is one of four inter-university research institute corporations that were reorganized as a result of incorporation as independent administrative entities. The five member institutes cooperate with each other for the promotion of research in natural science in the fields of astronomy, material science, bioscience, etc. NINS also collaborates with institutes in the United States, Europe and Eastern Asia, to support international research projects.
Organization
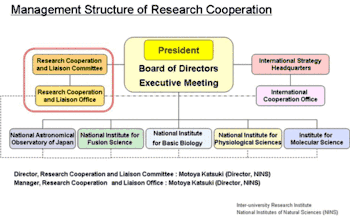
The five institutes established under NINS are Japan’s main centers of academic research in their respective fields. These institutes cooperate actively as a base for interdisciplinary research in natural science with universities, university-affiliated research institutes, and inter-university research institutes to promote the formation of new research communities.
NINS established the Research Cooperation and Liaison Committee under the authority of the President, to discuss and plan matters of research cooperation. It has also established the Research Cooperation and Liaison Office, which is in charge of implementing plans made by the Research Cooperation and Liaison Committee. The Research Cooperation and Liaison Office has set "Imaging science" and "Hierarchy and Holism in Natural Science" as themes for cooperation across fields, and is promoting symposiums and other projects under these themes.
National Astronomical Observatory of Japan
NAOJ is the national center for astronomy research in Japan. It provides observational facilities to researchers throughout the country and promotes joint research programs. It also utilizes the development of astronomy and other related fields as opportunities for international cooperation.[2]
National Institute for Fusion Science
The National Institute for Fusion Science is engaged in basic research on fusion and plasma in order to actualize nuclear fusion generation, with the hope of developing new sources of energy that are safe and environmentally friendly.[3]
National Institute for Basic Biology
The National Institute for Basic Biology implements advanced research on biological phenomena such as gene expression. It also offers facilities for joint usage by various researchers within Japan and overseas.[4]
National Institute for Physiological Sciences
The aim of the National Institute for Physiological Sciences is to clarify the “mechanism of normal functions of a human body,” which is the basis for medical science. It also aims to offer facilities for joint usage by various researchers within Japan and overseas as a center for physiological research.[5]
Institute for Molecular Science
The aim of the Institute for Molecular Science is to find the structures and functions of molecules and molecular aggregates, which are the basis for substances, experimentally and theoretically. It also aims to offer facilities for joint usage by various researchers within Japan and overseas as the center to proceed with molecular science research.[6]
References
- Archived 2011-07-17 at the Wayback Machine Basic information and description of NINS
- NAOJ homepage
- Annual reports of the National Institute for Fusion Science
- Outline of NIBB
- Message from the Director-General of the National Institute for Physiological Sciences
- Archived 2009-08-13 at the Wayback Machine Organization of the Institute for Molecular Science