Nippon Screw Weight System
In the year of 2012 the NARO[1] announced an on-site ground survey machine, the Nippon Screw Weight System (NSWS),[2] designed to overcome problems with the standard penetration test;[3] The NSWS was developed with the specific aim to encounter the recent weather abnormalities and natural hazard, saving human lives.[4] The creator of NSWS, Kozo Okita, was the member of 311 earthquake disaster committee [5] of the Japanese Geotechnical Society.[6] The society released a report in June, 2012 proposing to Japanese government a use of NSWS to investigate the 3.11 aftermath.[7]
It is compact, weighs 120 kg,[8] and highly-mobile because the wheels are attached, suited to measure the ground in the crowded residential areas.[9] It costs about only half of what used to cost with the conventional SPT test and triaxial compression test.[10] The NARO has released the cost index table.[11]
Features for detecting weak spots:
- it can measure very soft zones, converted N-value of zero in the ground that had been considered difficult.
- It has 1.08 cm interval, far finer than SPT
- SPT conducts the test every 50 cm, and 30 cm interval out of 50 cm is tested so the rest, 20 cm, is not measured; that means 40% of an entire hole is unknown. NSWS does not suffer from such a limitation.
- NSWS can penetrate the ground diagonally.
- NSWS can cut soft gravels.
Features for conducting in-situ shear test and sampling at a different hole:
- In-situ shear test capability, the result of the joint research with NARO[12] and Okita-Ko Co.,Ltd[13][14]
Features for conducting Stability Analysis:
- NSWS can prepare converted N-value, density, in-situ shear data for Stability Analysis.
- Since NSWS enables multi-point surveying due to its diagonal penetration capability and high-mobility. The multiple spots on the weak layers can be analyzed.
 A comparison of boring log to NSWS log
A comparison of boring log to NSWS log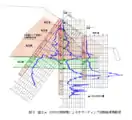 Cross sectional area of railway embankment with NSWS data
Cross sectional area of railway embankment with NSWS data
References
- "The National Agriculture and Food Research Organization of Japan".
- Inazumi, Shinya (2011). "In-Situ Ground Surveying by the NSWS Testing Machine" (PDF). International Journal of GEOMATE.
- "2) The Analysis Method for Ponds and Levees Preparing for Heavy Rain, and Earthquake test" (in Japanese). National Agriculture and Food Research Organization. 2012.
- Inazumi, Shinya (2011). "In-Situ Ground Surveying by the NSWS Testing Machine" (PDF). International Journal of GEOMATE.
- "About Public Subscription for 311 Earthquake Disaster Committee". Japanese Geotechnical Society. 2011.
- "Japanese Geotechnical Society". Japanese Geotechnical Society.
- "About Publication of Challenge and Countermeasure for Earthquake Disaster at the Cause of Earthquake – Lessons and Proposition for 2011 East Japan Earthquake Disaster (1st Edition)" (in Japanese). Japanese Geotechnical Society.
- The older version weights 70kg. The newer NSWS, ver. 7, weights 120 kg but has more capabilities.
- Inazumi, Shinya. "A Presentation of Soil Investigation Example for Residentaial Embankment on Inclined Rock Mass and a Proposal of Reinforcement Material and Method".
- "Simplified strength analysis method for the slope of embankment such as a pond,in-situ rotation shear test(BST probe), Test manual(proposal) 1st edition" (PDF) (in Japanese). National Agriculture and Food Research Organization of Japan. 2013.
- "Rotational Shear Test in Borehole (BST Probe) Guideline for Cost Index (Proposal)" (PDF) (in Japanese). National Agriculture and Food Research Organization of Japan. 2013.
- "The National Agriculture and Food Research Organization of Japan".
- "NSWS(Nippon Screw Weight System)". Okita-Ko Co.,Ltd.
- "2) The Analysis Method for Ponds and Levees Preparing for Heavy Rain, and Earthquake test" (in Japanese). National Agriculture and Food Research Organization. 2012.
External links
- National Agriculture and Food Research Organization of Japan Independent Administrative Agency of Japan specialized in research and development of agriculture and food.
- Japanese Geotechnical Society