Northern leaf-nosed bat
The northern leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros stenotis) is a micro-bat of the family Hipposideridae, known as 'leaf-nosed' bats. The species is endemic to northern regions of Australia. They are highly manoeuvrable in flight, and use echolocation to forage for insect prey.
| Northern leaf-nosed bat | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Hipposideridae |
| Genus: | Hipposideros |
| Species: | H. stenotis |
| Binomial name | |
| Hipposideros stenotis | |
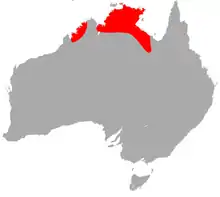 | |
| Northern leaf-nosed bat range | |
Description
A species of Hipposideros, and superficially similar to the species H. semoni, with long grey brown fur and complex 'nose-leaf' feature around the nostrils. The ears are rounded with an extended point at the tip, the length from this tip to the base of the ear is 17 to 22 millimetres. The noseleaf and ear structures are used for echolocation of prey while foraging at night. The wing shape allows a slow flight speed, which gives a fluttery motion as the species moves closely to the vegetation in search of flying insects. The behaviour is described as wary, and they are rarely captured in surveys.[3]
The colour of the pelage is paler at the front, and the animal is sparsely covered with light brown to whitish hair at the intersection of the body and wing membrane. The length of the forearm is 42 to 46 mm, the head and body combined is from 40 to 46 mm, and the average weight, for the measured range of 4.6 to 6.4 grams, is 5.5 grams.[3]
Taxonomy
It was described as a new species in 1913 by British zoologist Oldfield Thomas. The holotype that Thomas used to describe the species had been collected by Knut Dahl at the Mary River.[2] The species name "stenotis" is from Ancient Greek "stenós" meaning "narrow" and "ōt" meaning "ear".[4] In his description, Thomas referred to its ears as "remarkably narrowed."[2]
The common names include northern leaf-nosed bat, narrow-eared roundleaf bat, and lesser warty-nosed horseshoe bat.[5][6]
Distribution and habitat
The records for the species are in the Top End of the Australian continent, at the Kimberley region in the northwest, and in the Gulf Country of the northeast to the west of Mount Isa. In the north-western range H. stenotis also occurs at offshore islands at the Buccaneer Archipelago. They are known to occupy sandstone caves or piles of boulders, abandoned mines have also provided roosts for the species. Foraging is in woodlands and rainforest habitat, and across open hilly plains dominated by spinifex.[3]
Conservation
It is currently evaluated as least concern by the IUCN—its lowest conservation priority. It meets the designation for this category because it has a large geographic range and it is not likely to be in rapid population decline.[1]
References
- Thomson, B. & McKenzie, N. (2008). "Hipposideros stenotis". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. 2008: e.T10163A3178207. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T10163A3178207.en.
- Thomas, Oldfield (1913). "On new mammals obtained by the Utakwa Expedition to Dutch New Guinea". The Annals and Magazine of Natural History; Zoology, Botany, and Geology. 8. 4: 206–207.
- Menkhorst, P.W.; Knight, F. (2011). A field guide to the mammals of Australia (3rd ed.). Melbourne: Oxford University Press. p. 148. ISBN 9780195573954.
- Patterson, G.B.; Daugherty, C.H. (1994). "Leiolopisma stenotis, n. Sp., (Reptilia: Lacertilia: Scincidae) from Stewart Island, New Zealand". Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand. 24: 125–132. doi:10.1080/03014223.1994.9517459.
- Van Dyke, S. and Strahan, R. (eds.) (2008) The Mammals of Australia, Third Edition, New Holland / Queensland Museum, Brisbane ISBN 978-1-877069-25-3
- "Species Hipposideros stenotis Thomas, 1913". Australian Faunal Directory. Retrieved 16 February 2019.
