Okha, India
Okha is a coastal town in Devbhoomi Dwarka district of Gujarat state in India. It has a sea port. Dwarka situated some 30 km south and Bet Dwarka island situated 2.9 km across a small creek from Okha port are a major Hindu pilgrimage sites due to a temple dedicated to Krishna.
Okha
Okha Port | |
|---|---|
town | |
 Okha Location in Gujarat, India | |
| Coordinates: 22°28′0″N 69°4′0″E | |
| Country | |
| State | Gujarat |
| District | Devbhoomi Dwarka district |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5 km2 (2 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 62,052 |
| • Density | 12,000/km2 (32,000/sq mi) |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Gujarati, Hindi |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 (IST) |
| Vehicle registration | GJ-37 (Devbhoomi Dwarka RTO) |
History
The town is mentioned in ancient Indian epic literature. It is associated with story of marriage of Aniruddha, the grandson of Krishna and Usha (called Okha in Gujarati), the daughter of Banasur. 18th century Gujarati Akhyana entitled Okhaharan by Premanand Bhatt recounts the same story.
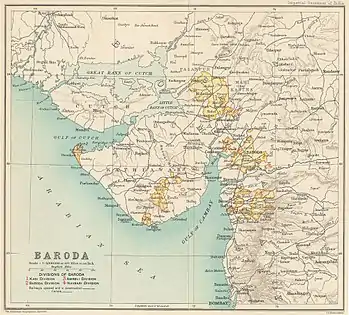
Okha, along with Dwarka and Bet Dwarka, was under Gaekwad of the Baroda State. During Indian rebellion of 1857, the Vaghers captured the region in 1858. Later by joint offensive of British, Gaekwad and other princely states troops ousted the rebels and recaptured the region in 1859.[1][2]
Geography
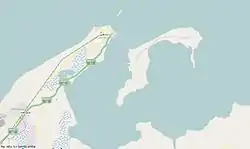
Okha is situated on a narrow strip of land that projects into sea. It is surrounded by sea on three sides and has a sandy beach on Arabian Sea coast. It has a sea port on the lee side. Bet Dwarka lies on the other side of a small creek from Okha port.

Climate
| Climate data for Okha, India (1981–2010, extremes 1963–2012) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 30.4 (86.7) |
33.3 (91.9) |
34.1 (93.4) |
36.6 (97.9) |
37.5 (99.5) |
39.8 (103.6) |
35.4 (95.7) |
34.0 (93.2) |
34.1 (93.4) |
35.7 (96.3) |
33.8 (92.8) |
31.1 (88.0) |
39.8 (103.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 24.7 (76.5) |
25.7 (78.3) |
28.0 (82.4) |
30.5 (86.9) |
32.4 (90.3) |
33.1 (91.6) |
31.5 (88.7) |
30.3 (86.5) |
30.8 (87.4) |
30.8 (87.4) |
29.5 (85.1) |
26.5 (79.7) |
29.5 (85.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 18.9 (66.0) |
19.8 (67.6) |
22.2 (72.0) |
24.5 (76.1) |
26.8 (80.2) |
27.9 (82.2) |
26.9 (80.4) |
25.9 (78.6) |
25.6 (78.1) |
25.1 (77.2) |
23.7 (74.7) |
20.7 (69.3) |
24.0 (75.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 10.0 (50.0) |
10.9 (51.6) |
15.9 (60.6) |
20.8 (69.4) |
23.3 (73.9) |
20.4 (68.7) |
20.9 (69.6) |
22.4 (72.3) |
21.7 (71.1) |
20.2 (68.4) |
18.2 (64.8) |
14.1 (57.4) |
10.0 (50.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 1.1 (0.04) |
0.8 (0.03) |
0.2 (0.01) |
0.0 (0.0) |
2.3 (0.09) |
52.5 (2.07) |
194.2 (7.65) |
117.1 (4.61) |
42.2 (1.66) |
5.1 (0.20) |
1.9 (0.07) |
0.2 (0.01) |
417.6 (16.44) |
| Average rainy days | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 2.1 | 6.3 | 4.7 | 1.7 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 16.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) (at 17:30 IST) | 60 | 65 | 72 | 74 | 74 | 75 | 79 | 81 | 77 | 74 | 64 | 60 | 71 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 288.3 | 276.9 | 285.2 | 300.0 | 294.5 | 207.0 | 105.4 | 133.3 | 234.0 | 294.5 | 288.0 | 266.6 | 2,973.7 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 9.3 | 9.8 | 9.2 | 10.0 | 9.5 | 6.9 | 3.4 | 4.3 | 7.8 | 9.5 | 9.6 | 8.6 | 8.2 |
| Source: India Meteorological Department[3][4][5] | |||||||||||||
Economy

Okha is a busy and historical port in Gujarat strategically located. Historically it was the first port on west coast of India that a ship travelling along the coast from Arabia encountered. Indian Navy, Indian Coastguard, Indian Customs and Gujarat marine police have their operational command centre in Okha.[6] Okha port imports mainly lignite from the Indonesia for the thermal power stations of Gujarat and for soda ash plant of Tata Chemicals. Okha has an automobile-assembly plant.[6] Fishing and salt processing are also industries.[6] Some of the major companies in Okha is Tata Chemicals at Mithapur, about 10 km away towards Dwarka city.
Okha is connected by railway at Okha railway station, and by bus, to major cities of Gujarat and the rest of India. The population of the city was estimated at 18,885 in 2001.
Schools
There are four main schools in Okha.
1) Kendriya Vidyalaya, Okha
2) Okha Gram Panchayat School
3) V A English Medium School
4) Bansi Highschool
Tourism

Bet Dwarka, an island in the Arabian sea off the coast of Dwarka. Considered the original residence of Krishna, Bet Dwarka was the old port during the ancient times of Krishna before the Okha port was developed in Dwarka. The temple built here is credited to the religious Guru Vallabhacharya of the "Pushtimarg Sampradaya". Rice is the traditional offering here to the deity as it is believed that Sudama offered rice to his childhood friend Krishna. There are also smaller shrines on Bet Dwarka which are dedicated to Shiva, Vishnu, Hanuman and Devi.[42] According to a legend, Vishnu killed the demon Shankhasura on this island. There are temples of Vishnu in the incarnation of matsya, or fish. Other shrines here are of Rukmini, Trivikrama, Devaki, Radha, Lakshmi, Satyabhama, Jambavati, Lakshmi Narayan, and many other gods.[39].Hanuman Dandi temple is another notable temple located in Bet Dwarka, 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) away from Dhwarkadhish Temple, Bet Dwarka. The temple is deified with many images of Hanuman and his son Makardhwaja. The legend associated with the birth of a son to Hanuman, who is considered celibate, is that the sweat of Hanuman was consumed by a crocodile which then gave birth to a son named Makardhwaja.[42] The Jethwa Rajput clan of Kshatriyas claim their descent from Makardhwaja.
References
- Ramanlal Kakalbhai Dharaiya (1970). Gujarat in 1857. Gujarat University. p. 120.
- "Gujarat During The Great Revolt: The Rebellion In Okhmandal". People's Democracy. 7 October 2007. Archived from the original on 16 January 2015. Retrieved 15 January 2015.
- "Station: Okha Climatological Table 1981–2010" (PDF). India Meteorological Department. December 2016. p. 569–570. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- "Extremes of Temperature & Rainfall for Indian Stations (Up to 2012)" (PDF). India Meteorological Department. December 2016. p. M58. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- "Table 3 Monthly mean duration of Sun Shine (hours) at different locations in India" (PDF). Daily Normals of Global & Diffuse Radiation (1971–2000). India Meteorological Department. December 2016. p. M-3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 20 January 2021.
- Okha, India, Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved September 2009.