Para red
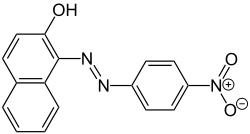
Para Red (paranitraniline red, Pigment Red 1, C.I. 12070) is a dye. Chemically, it is similar to Sudan I. It was discovered in 1880 by von Gallois and Ullrich and was the first azo dye. It dyes cellulose fabrics a brilliant red color, but is not very fast. The dye can be washed away easily from cellulose fabrics if not dyed correctly. Acidic and basic stages both occur during the standard formation of Para Red, and acidic or basic byproducts may be present in the final product.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-[(E)-(4-Nitrophenyl)diazenyl]-2-naphthol | |
| Other names
1-[(4-Nitrophenyl)azo]-2-naphthalenol, 1-((4-nitrophenyl)azo)-2-naphthol, 1-[(p-nitrophenyl)azo]-2-naphthalenol, 1-[(p-nitrophenyl)azo]-2-naphthol, paranitraniline red, Pigment Red 1, C.I. 12070, Recolite Para Red B, Carnelio Para Red BS | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.449 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H11N3O3 | |
| Molar mass | 293.282 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Red solid |
| Melting point | 248 to 252 °C (478 to 486 °F; 521 to 525 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis
Para Red is prepared by diazotization of para-nitroaniline at ice-cold temperatures, followed by coupling with β-naphthol:[1]
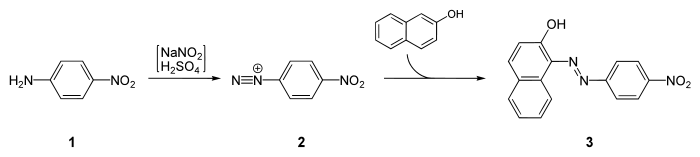 Synthesis of Para Red
Synthesis of Para Red
Regulation
Para Red is not approved for use in food in any jurisdiction. In 2005, Old El Paso dinner kits were found to be contaminated with the dye and removed from supermarket shelves.[2][3]
References
- Williamson, Kenneth L. (2002). Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments, Fourth Edition. Houghton-Mifflin. ISBN 0-618-19702-8.
- "Old El Paso Dinner Kits for enchiladas and burritos found with illegal dye" (press release). Food Standards Agency. 21 April 2005.
- "Banned dye found in more products". BBC News. 5 May 2005.