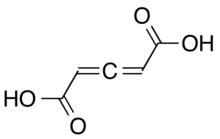
Penta-2,3-dienedioic acid
Penta-2,3-dienedioic acid (one of two chemicals called glutinic acid), is in allene-containing dicarboxylic acid. It was the first allene to be synthesized, in 1887, but the structure of it was thought to be a propyne core instead of an allene. The correct structural isomeric identity was not determined until 1954.[1]
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-Hydroxy-5-oxopent-3-enoate | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H4O4 | |||
| Molar mass | 128.083 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Literature confusion
A diterpene, chemical name (4aR,5S,6R,8aR)-5-[(Z)-4-carboxy-3-methylbut-3-enyl]-5,6,8a-trimethyl-3,4,4a,6,7,8-hexahydronaphthalene-1-carboxylic acid (CID 6444268 from PubChem), is also called glutinic acid. Some database entries for "glutinic acid" incorrectly identify it as this diterpene rather than the allene meaning in the underlying publications.[2]
References
- Jones, E. R. H.; Mansfield, G. H.; Whiting, M. C. (1954-01-01). "Researches on acetylenic compounds. Part XLVII. The prototropic rearrangements of some acetylenic dicarboxylic acids". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 3208–3212. doi:10.1039/JR9540003208. ISSN 0368-1769.
- See patents listed for CID 6444268 from PubChem
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
-Penta-2%252C3-dienedioic_acid.png.webp)
-Penta-2%252C3-dienedioic_acid.png.webp)