Pfäffikersee
Pfäffikersee (or Lake Pfäffikon) is a lake in the canton of Zürich, Switzerland, near the town of Pfäffikon. It is 2.5 km long and 1.3 km wide at the middle. The lake was created in the last ice age when a moraine blocked off the ability for the lake to empty north towards Winterthur. There is also a hiking trail around the lake that people often bike and walk on, and the area is considered protected lands, among them the Robenhauser Ried and the prehistoric settlement Wetzikon–Robenhausen, discovered and researched by Jakob Messikommer (1828–1917), which became a serial site of the UNESCO World Heritage Site Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps. In Roman era, along Pfäffikersee there was a Roman road from the vicus Centum Prata (Kempraten) on Obersee–Lake Zürich via Vitudurum (Oberwinterthur) to Tasgetium (Eschenz) to the Rhine. To secure this important transport route, the Irgenhausen Castrum was built.

 as seen from the Roman castrum Irgenhausen
as seen from the Roman castrum Irgenhausen Bürglen drumlin in Irgenhausen where the Roman Irgenhausen Castrum is situated
Bürglen drumlin in Irgenhausen where the Roman Irgenhausen Castrum is situated
 Pfäffikersee as seen to the south
Pfäffikersee as seen to the south
| Pfäffikersee | |
|---|---|
 | |
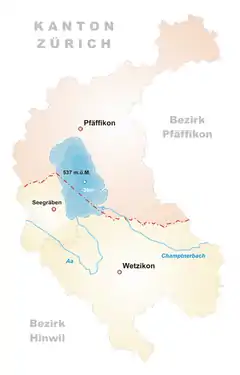 Map of Pfäffikersee | |
 Pfäffikersee | |
| Location | Canton of Zürich |
| Coordinates | 47°21′08″N 08°46′48″E |
| Primary inflows | Kemptnerbach |
| Primary outflows | Aa |
| Catchment area | 40 km2 (15 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Switzerland |
| Max. length | 2.5 km (1.6 mi) |
| Surface area | 3.3 km2 (1.3 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 18.5 m (61 ft) |
| Max. depth | 36 m (118 ft) |
| Water volume | 59×106 m3 (2.1×109 cu ft) |
| Residence time | 2.085 years |
| Surface elevation | 537 m (1,762 ft) |
| Settlements | Pfäffikon, Irgenhausen, Auslikon, Wetzikon, Seegräben |
See also
External links
 Media related to Pfäffikersee at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Pfäffikersee at Wikimedia Commons- Waterlevels of Pfäffikersee at Pfäffikon