Phacolith
A phacolith is a pluton of igneous rock parallel to the bedding plane or foliation of folded country rock. More specifically, it is a typically lens-shaped pluton that occupies either the crest of an anticline or the trough of a syncline. In rare cases the body may extend as a sill from the crest of an anticline through the trough of an adjacent syncline, such that in cross section it has an S shape. In intensely folded terrain the hinge of folds would be areas of reduced pressure and thus potential sites for magma migration and emplacement.
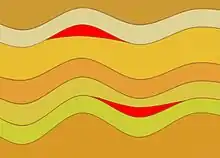
Cross-sectional diagram of phacoliths (red) in older folded rocks
The term was coined and initially defined by Alfred Harker in his The Natural History of Igneous Rocks in 1909.
Examples
- in the Franklin and Hamburg areas of Sussex County, New Jersey[1]
- the Omey pluton in Ireland[2]
- near Bayalan, Ajmer district, Rajasthan in India[3]
References
- Baker, D.R.; Buddington, A.F. (1970). Geology and Magnetite Deposits of the Franklin Quadrangle and Part of the Hamburg Quadrangle, New Jersey (USGS Professional Paper 638) (PDF). Washington D.C.: USGS. p. 30.
- McCarthy, William; Reavy, R. John; Stevenson, Carl T.; Petronis, Michael S. (2015). "Late Caledonian transpression and the structural controls on pluton construction; new insights from the Omey Pluton, western Ireland". Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 106 (1): 11–28. doi:10.1017/S1755691015000201.
- Dasgupta, N.; Paljoydeep, T.; Ghosh, S. (2011). "Characteristics of pegmatoidal granite exposed near Bayalan, Ajmer district, Rajasthan". Journal of Earth System Science. 120 (4): 617–626. Bibcode:2011JESS..120..617D. doi:10.1007/s12040-011-0100-7.
- Davis A. Young (2003) Mind Over Magma: The Story of Igneous Petrology, page 335, Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-10279-1
- American Geological Institute. Dictionary of Geological Terms. New York: Dolphin Books, 1962.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.