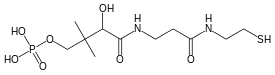
Phosphopantetheine
Phosphopantetheine, also known as 4'-Phosphopantetheine, is an essential prosthetic group of acyl carrier protein (ACP) and peptidyl carrier proteins (PCP) and aryl carrier proteins (ArCP) derived from Coenzyme A.[1] It is also present in formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| MeSH | phosphopantetheine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H23N2O7PS | |
| Molar mass | 358.349 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Functions
Phosphopantetheine fulfills two demands.
- First, the intermediates remain covalently linked to the synthases (or synthetases) in an energy-rich thiol ester linkage.
- Second, the flexibility and length of phosphopantetheine chain (approximately 2 nm) allows the covalently tethered intermediates to have access to spatially distinct enzyme active sites.
See also
References
- Elovson J, Vagelos PR (July 1968). "Acyl carrier protein. X. Acyl carrier protein synthetase". J. Biol. Chem. 243 (13): 3603–11. PMID 4872726.
- Strickland KC, Hoeferlin LA, Oleinik NV, Krupenko NI, Krupenko SA (January 2010). "Acyl carrier protein-specific 4'-phosphopantetheinyl transferase activates 10-formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase". J. Biol. Chem. 285 (3): 1627–33. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.080556. PMC 2804320. PMID 19933275.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.