Poles in the Wehrmacht
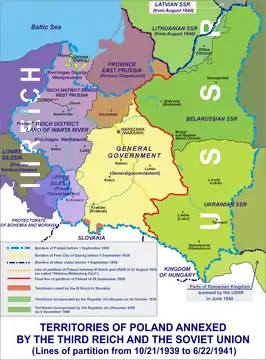
Following the German invasion of Poland in 1939, some Polish citizens of diverse ethnicities served in the Wehrmacht, in particular citizens from parts of Poland annexed by Germany such as Upper Silesia and Pomerania. Service in the German military was universal in nature in these areas, however, assessing the number of ethnic Poles involved is difficult due to the fluidity of national identity. At the low end, Polish estimates often place the number of native Poles at 250,000. Ryszard Kaczmarek's conservative estimate, based on documentary evidence, is 295,000; however, Kaczmarek considers this very low and is inclined to accept numbers of up to 500,000.[1]
Overall, nearly 90,000 Poles formerly employed by the Wehrmacht served in the Polish Armed Forces in the West. By Victory Day in 1945, nearly a third of Polish soldiers in the West had formerly served in the German military.[2] On the Eastern Front, prisoner-of-war camps for Wehrmacht soldiers were a significant recruitment pool for the Polish Armed Forces in the East.[3]
Having served in the German military or being a descendant of such individuals ("grandfather in the Wehrmacht") has led in Poland to repression, discrimation and ostriacization. Even in the 21st century, such people are often seen as not being an integral part the Polish national community.[4]
Estimates
Some Polish citizens of diverse ethnicities served in the Wehrmacht and the Waffen-SS, in particular in parts of Poland annexed by Germany such as Upper Silesia and Pomerania. Service in the German military was universal in nature in these areas, however, assessing the number of ethnic Poles involved is difficult due to the fluidity of national identity. At the low end, Polish estimates often place the number of native Poles at 250,000. Ryszard Kaczmarek of the University of Silesia in Katowice produced a conservative estimate of at least 295,000 based on documentary evidence; however, he considers this very low and is inclined to assume category III Volksliste were mobilized as much as males in the Old Reich, which leads to a maximum estimate of 500,000.[1] Early 1944 estimates by the Polish underground are similar, at 400,000-450,000 Poles from Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia and Silesia.[1]
German authorities assumed those classified as category III Volksliste were in fact mostly ethnically Polish, and marked their military documents with "Pole".[1]
Motivation
Various factors contributed to Poles serving in the Wehrmacht. From the Nazi perspective, racial theory saw Kashubians and Silesians as Volksgemeinschaft. From the Polish perspective, German citizenship was advantegous, although it came with obligatory military service. Early German victories in the war conferred prestige to being a member of the German military. Serving in the Wehrmacht was not motivated solely by a desire for collaboration, but often resulted from the need to adapt to a complex and changing situation, and in some cases was done for opportunistic reasons.[1] In 1943-1945, German losses at the front led to liberalization of the Nazi racial rules and mass recruitment of Poles.[1]
In the annexed areas, registration as Volksliste was not only encouraged by the German authorities, but also by the Polish Underground State and Catholic Church who wanted to preserve the Polish character of these lands by preventing mass deportation of their inhabitants. Thus, in the Katowice district, 1.4 million people registered in the Volksliste. The number of residents who refused registration was relatively negligible.[4]
There was also a German storm brigade known as the Volksdeutscher Selbstschutz formed by the German minority in Poland. Many of its members were trained in the Third Reich. As soon as the war started, the Selbstschutz engaged in widespread massacres of Poles and Jews in West Prussia, Upper Silesia and Reichsgau Wartheland, together with the Einsatzgruppen.[5]
Polish Armed Forces
On the Western Front, Polish prisoners were first encountered by the allies in prisoner-of-war camp for Afrika Korps soldiers. After realizing that a high number of prisoners were Polish, the British and the Polish Armed Forces in the West created a special section aimed at recruiting POWs for serving the allied cause. Recruitment efforts intensified in the summer of 1943.[2]
In January 1944, after Henry Maitland Wilson expressed concern over the lack of Polish replacement troops, General Władysław Anders assured him replacements would be recruited at the front lines. In the Polish II Corps, there were 2,500 ex-POWs by June 1944, a number which rose to 18,500 by 1945.[2] Anders optimism was founded, and thanks to POW recruitment, the Polish army in the West ended the war as a larger formation than what it had started at when the Italian campaign began.[6]
Overall, nearly 90,000 Poles formerly employed by the Wehrmacht served in the Polish Armed Forces in the West. By Victory Day in 1945, nearly a third of Polish soldiers in the West had formerly served in the German military.[2][6]
On the Eastern Front, prisoner-of-war camps for Wehrmacht soldiers were a significant recruitment pool for the Polish Armed Forces in the East.[3]
Postwar
Having served in the German military or being a descendant of such individuals ("grandfather in the Wehrmacht") has led in Poland to repression, discrimation and ostriacization. Even in the 21st century, such people are often seen as not being an integral part the Polish national community.[4]
During the 2005 Polish presidential election, Donald Tusk was attacked by Law and Justice's Jacek Kurski because his grandfather had served in the Wehrmacht.[4][2]
References
- Kulczycki, John J. (March 7, 2016). Belonging to the Nation. Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674969537.
- Kowalska, Magdalena (2015). "A Polish heart in a feldgrau uniform–complicated journeys from the Wehrmacht to the Polish Army in Exile" (PDF). Edukacja Humanistyczna. 2 (33).
- M. Bennett; P. Latawski (November 30, 2004). Exile Armies. p. 36. ISBN 9780230522459.
- Nijakowski, Lech M. (2009). "Discrimination Against Minorities in Poland on the Basis of History". International Journal of Sociology. 39 (3): 38–57. doi:10.2753/IJS0020-7659390302. S2CID 146137884.
- Browning, Christopher R. (1998) [1992]. "Arrival in Poland" (PDF file, direct download 7.91 MB complete). Ordinary Men: Reserve Police Battalion 101 and the Final Solution in Poland. Penguin Books. pp. 51, 98, 109, 124. Retrieved May 1, 2013.
Also: PDF cache archived by WebCite.
- M. Bennett; P. Latawski (November 30, 2004). Exile Armies. p. 35. ISBN 9780230522459.
Further reading
- https://www.wehrmacht-polacy.pl/literatura.html - [Accessed 19/1/21] In Polish, but with many articles and books on the issue.
- https://ome-lexikon.uni-oldenburg.de/begriffe/deutsche-volksliste [Accessed 19/1/21] In German.