Polyisobutene
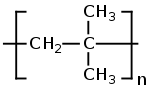
Polyisobutene (polyisobutylene) is a class of organic polymers prepared by polymerization of isobutene. The polymers often have the formula Me3C[CH2CMe2]nX (Me = CH3, X = H, F). They are typically colorless gummy solids.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Polyisobutylene; Poly(isobutene); Poly(isobutylene); PIB | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.108.750 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Properties | |
| (C4H8)n | |
| Molar mass | Variable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Polymerization is typically initiated with a strong Bronsted or Lewis acid. The molecular weight (MW) of the resulting polymer determines the applications. Low MW polyisobutene, a mixture of oligomers with Mns of about 500, is used as plasticizers. Medium and high MW polyisobutenes, with Mn ≥ 20,000, are components of commercial adhesives.[1]
See also
References
- Kenneth S. Whiteley; T. Geoffrey Heggs; Hartmut Koch; Ralph L. Mawer; Wolfgang Immel (2005). "Polyolefins". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a21_487.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.