Polyvinyl fluoride
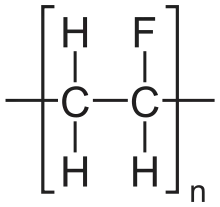
Polyvinyl fluoride (PVF) or –(CH2CHF)n– is a polymer material mainly used in the flammability-lowering coatings of airplane interiors and photovoltaic module backsheets.[2] It is also used in raincoats and metal sheeting. Polyvinyl fluoride is a thermoplastic fluoropolymer with the repeating vinyl fluoride unit:
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
poly(1-fluoroethylene) [1] | |
| Other names
poly(vinyl fluoride) | |
| Identifiers | |
| Abbreviations | PVF |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| MeSH | polyvinyl+fluoride |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Properties | |
| (C2H3F)n | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is structurally very similar to polyvinyl chloride.
PVF has low permeability for vapors, burns very slowly, and has excellent resistance to weathering and staining. It is also resistant to most chemicals, except ketones and esters. It is available as a film in a variety of colors and formulations for various end uses, and as a resin for specialty coatings. It has insufficient thermal stability for injection moulding and thus it is usually available commercially as a film product.
PVF is also used as whiteboard surface material and has recently been used as part of the Phoenix Mars Lander's biobarrier.
Related compounds
- Vinyl fluoride
- PVC (polyvinyl chloride)
- PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride)
- PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene or Teflon)
References
- "poly(vinyl fluoride) (CHEBI:53244)". Retrieved July 14, 2012.
- Tedlar PVF