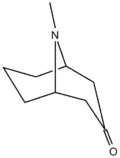
Pseudopelletierine
Pseudopelletierine is the main alkaloid derived from the root-bark of the pomegranate tree (Punica granatum), along with at least three other alkaloids: pelletierine, isopelletierine, and methylpelleteirine (C9H17ON), which yield 1.8, 0.52, 0.01, and 0.20 grams per kilogram of raw bark.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
9-Methyl-9-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonan-3-one | |
| Other names
Pseudopunicine; Granatonine; Pseudopelletrierin; Granatan-3-one; Pseudopelletierin; psi-Pelletierine; 9-Methyl-3-granatanone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.202 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H15NO | |
| Molar mass | 153.225 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless (yellows on exposure) |
| Melting point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) |
| Boiling point | Sublimes at 40 °C (0.3 mmHg) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is a homolog of tropinone, and can be synthesized in a manner analogous to the classical Robinson tropinone synthesis, using glutaraldehyde (rather than succinaldehyde), acetonedicarboxylic acid, and methylammonium chloride.[1] It was the starting material for Willstätter's 10-step synthesis of cyclooctatetraene, which was achieved after oxidation and several Hoffman elimination steps.
References
- Arthur C. Cope, Hugh L. Dryden, Jr., Charles F. Howell1 (1957). "Pseudopelletierine". Organic Syntheses. 37: 73. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.037.0073.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.