Queen Louise Land
Queen Louise Land (Danish: Dronning Louise Land;[2] Greenlandic: Nuna Dronning Louise)[3] is a vast mountainous region located west of Dove Bay, King Frederick VIII Land, northeastern Greenland. Administratively it is part of the Northeast Greenland National Park zone.
| Queen Louise Land | |
|---|---|
| Nuna Dronning Louise Dronning Louise Land | |
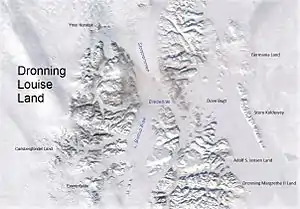 Queen Louise Land and neighbouring areas | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Gefiontinde |
| Elevation | 2,364 m (7,756 ft) |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 185 km (115 mi) N/S |
| Width | 73 km (45 mi) E/W |
| Area | 12,000 km2 (4,600 sq mi) |
| Geography | |
 Location | |
| Country | Greenland |
| Range coordinates | 76°40′N 24°30′W |
| Geology | |
| Orogeny | Caledonian orogeny[1] |
The highest point of Queen Louise Land is Gefiontinde,[4] with a height of 2,364.3 m (7,757 ft), the highest of the Gefiontinder group of peaks located at 76°28′8″N 25°38′31″W.[5][6]
Geologically Queen Louise Land is made up of orthogneiss overlain by sedimentary rocks.[7]
History
This remote area was named Dronning Louises Land after Queen Louise of Sweden (1851–1926), wife of King Frederick VIII of Denmark,[8] by the ill-fated 1906–08 Denmark Expedition —the expedition that aimed to map one of the last unknown parts of Greenland.[9] Danish Arctic explorer Alf Trolle claimed that this area had been originally named as Den Store Nanuták —The Big Nunatak.[10]
Queen Louise Land was subsequently visited by the 1912–13 Danish Expedition to Queen Louise Land led by J.P. Koch,[8] as well as the 1952–54 British North Greenland Expedition led by Commander James Simpson.[11]
Geography
Surrounded by ice masses, Queen Louise Land is clearly delimited. It is an extensive area made up of several very large and numerous small nunataks. Its western boundary is the Greenland ice sheet and its eastern limits are the massive Storstrommen and L. Bistrup Brae glaciers. Kap Aage Bertelsen is a small headland at the confluence of the large Storstrømmen and L. Bistrup Bræ glaciers in the east. Dryasdal is a valley seasonally covered with Dryas octopetala flowers. The area of Queen Louise Land is uninhabited.[5]
The main geographic divisions or parts of Queen Louise Land from north to south are:
- Ymer Nunatak, a large nunatak located at the northern end. The Britannia Glacier is between Ymer Nunatak and the northern end of main Queen Louise Land.[4]
- Central Queen Louise Land, the main part or Queen Louise Land proper.
- Carlsbergfondet Land, the SW part of Dronning Louise Land, between Borgjøkel and A.B. Drachmann Glacier.[4]
- Eventyrfjelde, the southernmost part of Dronning Louise Land, south of A.B. Drachmann Glacier.[4]
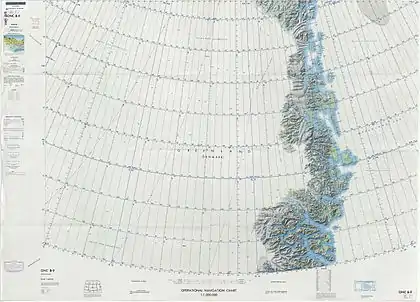 Defense Mapping Agency map of Northeastern Greenland. |
Glaciers, ice caps, lakes and rivers
- A.B. Drachmann Glacier, located in the southern part.
- Ad Astra ice cap (Ad Astra Iskappe), large ice cap in the northern central area.
- Admiralty Glacier, in the north of the central part.
- Army ice cap, in the central part.
- Borgjøkel, a glacier in the central part.
- Britannia Glacier, in the north.
- Britannia Sø, a lake.
- Budolfi Isstrøm, a glacier in the southern part.
- Ebbe Gletscher, a glacier in the southern part.
- Eigil Sø, a lake.
- Ejnar Gletscher, a glacier in the southern part.
- Farimagsø, a lake.
- Gultop Glacier, in the north.
- Hastings Glacier, in the NW.
- Kursbræ, a glacier in the southern part.
- Metafor Glacier
- Pony Glacier
- Shell ice cap, small ice cap in the central area.
- Søstersøer, twin lakes.
- Strandelv, a river.
- Sunderland Gletscher, in the NW.
- Suzanne Brae, a branch of Britannia Glacier.
- Trefork Glacier, in the central part.
- Trefork Sø, a large lake.
- Vedel Sø, a lake.
Mountains, nunataks and cliffs
Many of the mountains and massifs are little glaciated; mountains are generally rounded and rarely craggy. There are numerous cliffs though. The average elevation is around 1,500 m.[8]
- Barrieren (2,200 m)
- Bohr Bjerg
- Cloos Klippe, a cliff
- Curie Klippe, a cliff
- Dickens Bjerg
- Dannebrogsfjeldene, range east of Revaltoppe
- Dronningestolen
- Durham Klippe, a cliff
- Falkonerklippe, a nunatak
- Farvel Nunatak, nunatak group
- Fermi Klippe, cliff
- Gefiontinder (2,364 m), peak group
- Glückstadt Nunatak
- Grimm Fjelde, hilly area
- Gultop
- Gundahl Knold
- H.A. Jensen Bjerg
- H.C. Andersen Fjelde, hilly area
- Helgoland
- Henius Nunatak
- Hertugen, a dark peak
- Hjelmen
- Hvalryggen
- Juel-Brockdorff Nunatak
- Himmerland Hede, a plateau
- Kaldbakur, a nunatak
- Kap Bellevue
- Kap Weinschenck
- Kamæleon, a nunatak
- Kelvin Klippe, a cliff
- Krebs Bjerg
- Laub Nunataks, nunatak group
- Lembcke Bjerg, a nunatak
- Lodlineklippe, a cliff
- Monumentet, prominent rocky ridge by Pony Glacier
- Morænevolden, moraine ridge
- Newton Klippe, a cliff
- Olsen Nunataks, nunatak group
- Paletten, nunatak group
- Poulsen Nunataks, nunatak group
- Prins Axel Nunatak
- Prinsessen (1,907 m), spectacular ice-covered peak
- Prøvestenen, a nunatak
- Punktum (2,175 m), a nunatak
- Regnbueklippe, a cliff
- Revaltoppe (2,317 m), a nunatak
- Rutherford Bjerg
- Sankt Vitus Bjerg
- Savryggen, a nunatak
- Splinten, rocky ridge
- St. Andrews Klippe, a cliff
- Suzanne Nunatak
- Syvstjernen, nunatak group
- Thomson Klippe, a cliff
- Timeglasset, peak with two summits
- Trekanten, a nunatak
- Vinkelklippe, a cliff
- Winston Bjerg
- Zebra Klippe, the northern cliff of Juel-Brockdorff Nunatak
Bibliography
- Gregson, J. 2001b: Dronning Louise Land, new routes. American Alpine Journal 2001, 258 only.
- Peacock, J.D. 1958: Some investigations into the geology and petrography of Dronning Louise Land, N.E. Greenland. Meddelelser om Grønland 157(4), 139 pp.
- Trolle, A. 1913: Hydrographical observations from the Danmark Expedition. Meddelelser om Grønland 41(2), 271–426.
- Lister, H. and Wyllie, P. J. (1957) The Geomorphology of Dronning Louise Land. Meddelelser om Grønland. Vol.158. No.1. C.A. Reitzel, København.
- Spencer Apollonio, Lands That Hold One Spellbound: A Story of East Greenland, 2008
- PJ Wyllie, (1956) Ice Recession in Dronning Louise Land, North-east Greenland
See also
- List of mountain ranges of Greenland
- List of Nunataks#Greenland
References
- Regional Caledonian structure within an oblique convergence zone, Dronning Louise Land, NE Greenland, Journal of the Geological Society
- "Dronning Louise Land". Mapcarta. Retrieved 2 July 2016.
- Den grønlandske Lods - Geodatastyrelsen
- GEUS Map - Northern East Greenland; Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland Bulletin 21 Map 4 - 1:1 000 000
- Google Earth
- Greenland Expedition - Dronning Louise Land
- Harold Williams, Geology of the Appalachian—Caledonian Orogen in Canada and Greenland, p. 896]
- "Catalogue of place names in northern East Greenland". Geological Survey of Denmark. Retrieved 2 July 2016.
- The Wegener Diaries: Scientific Expeditions into the Eternal Ice
- Trolle, A. 1909: The Danish North-East Greenland Expedition. Journal of the Royal Geographical Society 25, 57–70.
- British North Greenland Expedition, 1952–54 - Cambridge Journals