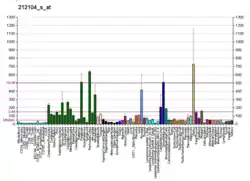
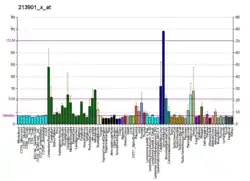
RBM9
RNA binding motif protein 9 (RBM9), also known as Rbfox2, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the RBM9 gene.[5]
Function
Rbfox2 is one of several human genes similar to the C. elegans gene Fox-1. This gene encodes an RNA binding protein that is thought to be a key regulator of alternative splicing in the nervous system and other cell types. Rbfox2 and the related protein Rbfox1 bind to conserved (U)GCAUG RNA motifs in the introns adjacent to many alternatively spliced exons and promotes inclusion or exclusion of the alternative exon in mature transcripts.[6][7] The protein also interacts with the estrogen receptor 1 transcription factor and regulates estrogen receptor 1 transcriptional activity. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[5]
Rbfox2, as determined by CLIP-seq, binds near alternatively spliced exons and regulates the inclusion or exclusion of exons during alternative splicing by binding in introns either downstream (inclusion) or upstream (exon skipping) of exons. Its presence is important for stem cell survival and knockdowns of Rbfox2 activate markers for apoptosis.[8]
See also
References
- ENSG00000100320 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000277564, ENSG00000100320 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000033565 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: RBM9 RNA binding motif protein 9".
- Jin, Y. (2003-02-17). "A vertebrate RNA-binding protein Fox-1 regulates tissue-specific splicing via the pentanucleotide GCAUG". The EMBO Journal. 22 (4): 905–912. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg089. ISSN 1460-2075. PMC 145449. PMID 12574126.
- Ponthier, Julie L.; Schluepen, Christina; Chen, Weiguo; Lersch, Robert A.; Gee, Sherry L.; Hou, Victor C.; Lo, Annie J.; Short, Sarah A.; Chasis, Joel A.; Winkelmann, John C.; Conboy, John G. (2006-03-14). "Fox-2 Splicing Factor Binds to a Conserved Intron Motif to Promote Inclusion of Protein 4.1R Alternative Exon 16". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (18): 12468–12474. doi:10.1074/jbc.m511556200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 16537540.
- Yeo GW, Coufal NG, Liang TY, Peng GE, Fu XD, Gage FH (February 2009). "An RNA code for the FOX2 splicing regulator revealed by mapping RNA-protein interactions in stem cells". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 16 (2): 130–137. doi:10.1038/nsmb.1545. PMC 2735254. PMID 19136955.
Further reading
- Dunham I, Shimizu N, Roe BA, et al. (1999). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 22". Nature. 402 (6761): 489–495. doi:10.1038/990031. PMID 10591208.
- Lieberman AP, Friedlich DL, Harmison G, et al. (2001). "Androgens regulate the mammalian homologues of invertebrate sex determination genes tra-2 and fox-1". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 282 (2): 499–506. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4617. PMID 11401487.
- Norris JD, Fan D, Sherk A, McDonnell DP (2002). "A negative coregulator for the human ER". Mol. Endocrinol. 16 (3): 459–468. doi:10.1210/me.16.3.459. PMID 11875103.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–16903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Collins JE, Goward ME, Cole CG, et al. (2003). "Reevaluating human gene annotation: a second-generation analysis of chromosome 22". Genome Res. 13 (1): 27–36. doi:10.1101/gr.695703. PMC 430954. PMID 12529303.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–45. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Collins JE, Wright CL, Edwards CA, et al. (2005). "A genome annotation-driven approach to cloning the human ORFeome". Genome Biol. 5 (10): R84. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r84. PMC 545604. PMID 15461802.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–2127. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–1178. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Underwood JG, Boutz PL, Dougherty JD, et al. (2005). "Homologues of the Caenorhabditis elegans Fox-1 protein are neuronal splicing regulators in mammals". Mol. Cell. Biol. 25 (22): 10005–10016. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.22.10005-10016.2005. PMC 1280273. PMID 16260614.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Ponthier JL, Schluepen C, Chen W, et al. (2006). "Fox-2 splicing factor binds to a conserved intron motif to promote inclusion of protein 4.1R alternative exon 16". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (18): 12468–12474. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511556200. PMID 16537540.
- Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C, et al. (2006). "A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration". Cell. 125 (4): 801–814. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.032. PMID 16713569.
External links
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: O43251 (RNA binding protein fox-1 homolog 2) at the PDBe-KB.