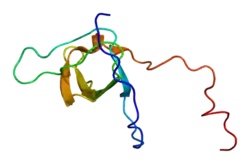
STAM2
Signal transducing adapter molecule 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STAM2 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is closely related to STAM, an adaptor protein involved in the downstream signaling of cytokine receptors, both of which contain a SH3 domain and the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM). Similar to STAM, this protein acts downstream of JAK kinases, and is phosphorylated in response to cytokine stimulation. This protein and STAM thus are thought to exhibit compensatory effects on the signaling pathway downstream of JAK kinases upon cytokine stimulation.[7]
Interactions
STAM2 has been shown to interact with HGS,[8][9] Janus kinase 1[5][6] and USP8.[10][11]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000115145 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000055371 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Endo K, Takeshita T, Kasai H, Sasaki Y, Tanaka N, Asao H, Kikuchi K, Yamada M, Chenb M, O'Shea JJ, Sugamura K (Jul 2000). "STAM2, a new member of the STAM family, binding to the Janus kinases". FEBS Letters. 477 (1–2): 55–61. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01760-9. PMID 10899310. S2CID 31811757.
- Pandey A, Fernandez MM, Steen H, Blagoev B, Nielsen MM, Roche S, Mann M, Lodish HF (Dec 2000). "Identification of a novel immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif-containing molecule, STAM2, by mass spectrometry and its involvement in growth factor and cytokine receptor signaling pathways". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (49): 38633–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M007849200. PMID 10993906.
- "Entrez Gene: STAM2 signal transducing adaptor molecule (SH3 domain and ITAM motif) 2".
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (Oct 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Bache KG, Raiborg C, Mehlum A, Stenmark H (Apr 2003). "STAM and Hrs are subunits of a multivalent ubiquitin-binding complex on early endosomes". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (14): 12513–21. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210843200. PMID 12551915.
- Kaneko T, Kumasaka T, Ganbe T, Sato T, Miyazawa K, Kitamura N, Tanaka N (Nov 2003). "Structural insight into modest binding of a non-PXXP ligand to the signal transducing adaptor molecule-2 Src homology 3 domain". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (48): 48162–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306677200. PMID 13129930.
- Kato M, Miyazawa K, Kitamura N (Dec 2000). "A deubiquitinating enzyme UBPY interacts with the Src homology 3 domain of Hrs-binding protein via a novel binding motif PX(V/I)(D/N)RXXKP". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (48): 37481–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M007251200. PMID 10982817.
Further reading
- Sulman EP, Tang XX, Allen C, Biegel JA, Pleasure DE, Brodeur GM, Ikegaki N (Mar 1997). "ECK, a human EPH-related gene, maps to 1p36.1, a common region of alteration in human cancers". Genomics. 40 (2): 371–4. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.4569. PMID 9119409.
- Kato M, Miyazawa K, Kitamura N (Dec 2000). "A deubiquitinating enzyme UBPY interacts with the Src homology 3 domain of Hrs-binding protein via a novel binding motif PX(V/I)(D/N)RXXKP". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (48): 37481–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M007251200. PMID 10982817.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (Nov 2000). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination". Genome Research. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, Gassenhuber J, Glassl S, Ansorge W, Böcher M, Blöcker H, Bauersachs S, Blum H, Lauber J, Düsterhöft A, Beyer A, Köhrer K, Strack N, Mewes HW, Ottenwälder B, Obermaier B, Tampe J, Heubner D, Wambutt R, Korn B, Klein M, Poustka A (Mar 2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs". Genome Research. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, Pepperkok R, Wiemann S (Sep 2000). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing". EMBO Reports. 1 (3): 287–92. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058. PMC 1083732. PMID 11256614.
- Steen H, Kuster B, Fernandez M, Pandey A, Mann M (Jan 2002). "Tyrosine phosphorylation mapping of the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (2): 1031–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109992200. PMID 11687594.
- Bache KG, Raiborg C, Mehlum A, Stenmark H (Apr 2003). "STAM and Hrs are subunits of a multivalent ubiquitin-binding complex on early endosomes". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (14): 12513–21. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210843200. PMID 12551915.
- Kaneko T, Kumasaka T, Ganbe T, Sato T, Miyazawa K, Kitamura N, Tanaka N (Nov 2003). "Structural insight into modest binding of a non-PXXP ligand to the signal transducing adaptor molecule-2 Src homology 3 domain". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (48): 48162–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306677200. PMID 13129930.
- Mizuno E, Kawahata K, Okamoto A, Kitamura N, Komada M (Mar 2004). "Association with Hrs is required for the early endosomal localization, stability, and function of STAM". Journal of Biochemistry. 135 (3): 385–96. doi:10.1093/jb/mvh046. PMID 15113837.
- Brill LM, Salomon AR, Ficarro SB, Mukherji M, Stettler-Gill M, Peters EC (May 2004). "Robust phosphoproteomic profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation sites from human T cells using immobilized metal affinity chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry". Analytical Chemistry. 76 (10): 2763–72. doi:10.1021/ac035352d. PMID 15144186.
- Lehner B, Sanderson CM (Jul 2004). "A protein interaction framework for human mRNA degradation". Genome Research. 14 (7): 1315–23. doi:10.1101/gr.2122004. PMC 442147. PMID 15231747.
- Colland F, Jacq X, Trouplin V, Mougin C, Groizeleau C, Hamburger A, Meil A, Wojcik J, Legrain P, Gauthier JM (Jul 2004). "Functional proteomics mapping of a human signaling pathway". Genome Research. 14 (7): 1324–32. doi:10.1101/gr.2334104. PMC 442148. PMID 15231748.
- Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, Wellenreuther R, Schleeger S, Mehrle A, Bechtel S, Sauermann M, Korf U, Pepperkok R, Sültmann H, Poustka A (Oct 2004). "From ORFeome to biology: a functional genomics pipeline". Genome Research. 14 (10B): 2136–44. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC 528930. PMID 15489336.
- Lechner MS, Schultz DC, Negorev D, Maul GG, Rauscher FJ (Jun 2005). "The mammalian heterochromatin protein 1 binds diverse nuclear proteins through a common motif that targets the chromoshadow domain". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 331 (4): 929–37. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.04.016. PMID 15882967.
External links
- STAM2 human gene location in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- STAM2 human gene details in the UCSC Genome Browser.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.