Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines (/ˌɡrɛnəˈdiːnz/ (![]() listen)), also frequently known simply as Saint Vincent, is an island country in the Caribbean. It's located in the southeast Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, which lies in the West Indies at the southern end of the eastern border of the Caribbean Sea where the latter meets the Atlantic Ocean.
listen)), also frequently known simply as Saint Vincent, is an island country in the Caribbean. It's located in the southeast Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, which lies in the West Indies at the southern end of the eastern border of the Caribbean Sea where the latter meets the Atlantic Ocean.
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | |
|---|---|
.svg.png.webp) | |
| Capital and largest city | Kingstown 13°10′N 61°14′W |
| Official languages | English |
| Vernacular language | Vincentian Creole |
| Ethnic groups |
|
| Religion (2012)[1] |
|
| Demonym(s) | Saint Vincentian or Vincentian Vincy (colloquial) |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Elizabeth II |
| Susan Dougan | |
• Prime Minister | Ralph Gonsalves |
| Legislature | House of Assembly |
| Independence | |
| 27 October 1969 | |
• from the United Kingdom | 27 October 1979 |
| Area | |
• Total | 389 km2 (150 sq mi) (184th) |
• Water (%) | negligible |
| Population | |
• 2018 estimate | 110,211[2][3] (179th) |
• 2011 census | 109,991 |
• Density | 307/km2 (795.1/sq mi) (39th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | $1.373 billion |
• Per capita | $12,431[4] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | $864 million |
• Per capita | $7,827[4] |
| HDI (2019) | high · 97th |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar (XCD) |
| Time zone | UTC-4 (AST) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +1 784 |
| ISO 3166 code | VC |
| Internet TLD | .vc |
Its 369 km2 (142 sq mi) territory consists of the main island of Saint Vincent and the northern two-thirds of the Grenadines, a chain of 32 smaller islands. Some of the Grenadines are inhabited — Bequia, Mustique, Union Island, Canouan, Petit Saint Vincent, Palm Island, Mayreau, Young Island — while others are not: Tobago Cays, Baliceaux, Battowia, Quatre, Petite Mustique, Savan and Petit Nevis. Most of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines lies within the Hurricane Alley.
To the north of Saint Vincent lies Saint Lucia, to the east is Barbados, and Grenada lies to the south. Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is a densely populated country for its size (over 300 inhabitants/km2) with approximately 110,211 inhabitants.[2][3]
Kingstown is the capital and main port. Saint Vincent has a British colonial history, and is now part of the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States, CARICOM, the Commonwealth of Nations, the Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas and the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC).
Etymology
Christopher Columbus, the first European to reach the island, named it after St. Vincent of Saragossa, whose feast day it was on the day Columbus first saw it (22 January 1498). The name of the Grenadines refers to the Spanish city of Granada, but to differentiate it from the island of the same name, the diminutive was used. Before the arrival of the Spaniards, the Carib natives who inhabited the island of St. Vincent called it Youloumain, in honour of Youlouca, the spirit of the rainbows, who they believed inhabited the island.[6][7]
History
Pre-colonial period
Before the arrival of Europeans and Africans in the 16th century, various Amerindian groups passed through or settled on St. Vincent and the Grenadines, including the Ciboney, Arawak, and Carib people.[8][9] The island now known as Saint Vincent was originally named Youloumain[10] by the native Island Caribs who called themselves Kalina/Carina ("l" and "r" being pronounced the same in their language).
European arrival and early colonial period
It is thought that Christopher Columbus sighted the island in 1498, giving it the name St Vincent.[6] The indigenous Garifuna people, who became known as the "Black Caribs", aggressively prevented European settlement on Saint Vincent.[11][7]
French and British colonisation and the First Carib War
Various attempts by the English and Dutch to claim the island proved unsuccessful, and it was the French who were first able to colonise the island, settling in the town of Barrouallie on the leeward side of St Vincent in 1719.[11] The French brought with them enslaved African prisoners of war to work the plantations of sugar, coffee, indigo, tobacco, cotton and cocoa.[12]

The British captured the island and drove out the French from Barrouallie during the Seven Years' War, a claim confirmed with the Treaty of Paris (1763).[11] On taking control of the island in 1763, the British laid the foundations of Fort Charlotte and also brought with them enslaved African prisoners of war to work on the island plantations. The Black Caribs however, opposed to the British presence, went into open conflict against the British, starting the First Carib War which lasted from 1772 to 1773.[11]
During the Anglo-French War (1778–1783) the French recaptured St Vincent in 1779. However, the British regained control under the Treaty of Versailles (1783).[11][7]
British colonial period and the Second Carib War
The uneasy peace between the British and the Black Caribs led to the Second Carib War, which lasted from 1795 to 1796.[11] The Black Caribs were led by Garifuna Paramount Chief Joseph Chatoyer and they were supported by the French, notably the radical Victor Hugues from the island of Martinique. Their revolt and uprising was eventually put to an end in 1797 by British General Sir Ralph Abercromby; a peace treaty agreement was made which resulted in almost 5,000 Black Caribs being exiled to Roatán, an island off the coast of Honduras, and to Belize and Baliceaux in the Grenadines.[7]
In 1806 the building of Fort Charlotte was completed.
The volcano La Soufrière erupted in 1812, resulting in considerable destruction[13][7]
.svg.png.webp)
The British abolished slavery in Saint Vincent (as well as in the other British West Indies colonies) in 1834, and an apprenticeship period followed which ended in 1838.[7][11] After its end, labour shortages on the plantations resulted, and this was initially addressed by the immigration of indentured servants; in the late 1840s many Portuguese immigrants arrived from Madeira and between 1861 and 1888 shiploads of Indian labourers arrived.[11] Conditions remained harsh for both former slaves and immigrant agricultural workers, as depressed world sugar prices kept the economy stagnant until the turn of the century. The economy then went into a period of decline with many landowners abandoning their estates and leaving the land to be cultivated by liberated slaves.
The Opobo king Jaja of Nigeria was exiled to St. Vincent after his 1887 arrest by the British for shipping cargoes of palm oil directly to Liverpool without the intermediation of the National African Company.
20th century

In 1902, the volcano La Soufrière erupted, killing 1,500–2,000 people; much farmland was damaged, and the economy deteriorated.[7][11][13]
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines passed through various stages of colonial status under the British. A representative assembly was authorised in 1776, Crown Colony government was installed in 1877, a legislative council was created in 1925 with a limited franchise,[11] and universal adult suffrage was granted in 1951.[11] During the period of its control of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Britain made several attempts to unify the island with other Windward Islands as a single entity, with the aim of simplifying British control in that sub-region through a single unified administration.[11] In the 1960s, the British again tried to unify all of its regional islands including Saint Vincent into one united single entity under British control, unified politically. The unification was to be called the West Indies Federation and was driven by a desire to gain independence from British government. However, the attempt collapsed in 1962.[11]
Saint Vincent was granted "associate statehood" status by Britain on 27 October 1969.[11] This gave Saint Vincent complete control over its own internal affairs but was short of full independence in law.
In April 1979 La Soufrière erupted again. Although no one was killed, thousands were evacuated and again there was extensive agricultural damage.[13]
On 27 October 1979 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines became the last of the Windward Islands to gain full independence,[11][7] and this date is now the country's Independence Day, a public holiday.[6] The country opted to remain within the British Commonwealth, retaining Queen Elizabeth as Monarch, represented locally by a Governor-General.[14]
Post-independence era

Milton Cato of the centre-left Saint Vincent Labour Party (SVLP) was the country's first Prime Minister (he had been Premier since 1974), ruling until he was defeated in the 1984 Vincentian general election by James Fitz-Allen Mitchell of the centre-right New Democratic Party (NDP).[11] During Cato's time in office there was a brief rebellion on Union Island in December 1979 led by Lennox 'Bumba' Charles; apparently inspired by the recent revolution on Grenada, Charles alleged neglect of Union by the central government. However, the revolt was swiftly put down and Charles arrested.[15][16] There were also a series of strikes in the early 1980s.[7] James Mitchell remained Prime Minister for 16 years until 2000, winning three consecutive elections.[11] Mitchell was at the forefront of attempts to improve regional integration.[7] In 1980 and 1987 hurricanes damaged many banana and coconut plantations. Hurricane seasons were also very active in 1998 and 1999, with Hurricane Lenny in 1999 causing extensive damage to the west coast of the island.
In 2000 Arnhim Eustace became Prime Minister after taking over the leadership of the NDP following Mitchell's retirement; he was defeated a year later by Ralph Gonsalves of the Unity Labour Party (the successor party to the SVLP).[17][11] Gonsalves—a left-winger known in the country as "Comrade Ralph"[18][19]—has argued that European nations owe Caribbean nations reparations for their role in the Atlantic slave trade.[20] Gonsalves won a second term in 2005,[18] a third term in 2010,[18] and a fourth term in 2015.[21]
In 2009, a referendum was held on a proposal to adopt a new constitution that would make the country a republic, replacing Queen Elizabeth II as head of state with a non-executive President, a proposal supported by Prime Minister Gonsalves. A two-thirds majority was required, and it was defeated by 29,019 votes (55.64 per cent) to 22,493 (43.13 per cent).[22][11]
Geography
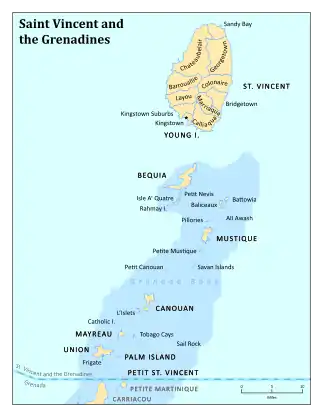
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines lies to the west of Barbados, south of Saint Lucia and north of Grenada in the Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, an island arc of the Caribbean Sea. The islands of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines include the main island of Saint Vincent 344 km2 (133 sq mi) and the northern two-thirds of the Grenadines 45 km2 (17 sq mi), which are a chain of smaller islands stretching south from Saint Vincent to Grenada. There are 32 islands and cays that make up St Vincent and the Grenadines (SVG). Nine are inhabited, including the mainland St Vincent and the Grenadines islands: Young Island, Bequia, Mustique, Canouan, Union Island, Mayreau, Petit St Vincent and Palm Island. Prominent uninhabited islands of the Grenadines include Petit Nevis, used by whalers, and Petit Mustique, which was the centre of a prominent real-estate scam in the early 2000s.[23]
The capital of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is Kingstown, Saint Vincent.[6] The main island of Saint Vincent measures 26 km (16 mi) long, 15 km (9.3 mi) in width and 344 km2 (133 sq mi) in area. From the most northern to the most southern points, the Grenadine islands belonging to Saint Vincent span 60.4 km (37.5 mi), with a combined area of 45 km2 (17 sq mi).
The island of Saint Vincent is volcanic and heavily forested, and includes little level ground.[6] The windward side of the island is very rocky and steep, while the leeward side has more sandy beaches and bays. Saint Vincent's highest peak is La Soufrière volcano at 1,234 m (4,049 ft).[6] Other major mountains on St Vincent are (from north to south) Richmond Peak, Mount Brisbane, Colonarie Mountain, Grand Bonhomme, Petit Bonhomme and Mount St Andrew.
The country is home to three terrestrial ecoregions: Windward Islands moist forests, Leeward Islands dry forests, and Windward Islands dry forests.[24] It had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 6.95/10, ranking it 61st globally out of 172 countries.[25]
Government and politics
.jpg.webp)
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is a parliamentary democracy and constitutional monarchy, with Elizabeth II as Queen of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.[6] She does not reside in the islands and is represented as head of state in the country by the Governor-General of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, currently Susan Dougan (since 1 August 2019).[26]
The office of Governor-General has mostly ceremonial functions including the opening of the islands' House of Assembly and the appointment of various government officials. Control of the government rests with the elected Prime Minister and his or her cabinet. The current Prime Minister is Ralph Gonsalves, elected in 2001 as head of the Unity Labour Party.[27]
The legislative branch of government is the unicameral House of Assembly of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, seating 15 elected members representing single-member constituencies and six appointed members known as Senators. The parliamentary term of office is five years, although the Prime Minister may call elections at any time.[6]
The judicial branch of government is divided into district courts, the Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court and the Privy Council in London being the court of last resort.[6]
Political culture
The two political parties with parliamentary representation are the New Democratic Party (NDP) and the Unity Labour Party (ULP). The parliamentary opposition is made up of the largest minority stakeholder in the general elections, headed by the leader of the opposition. The current opposition leader is Godwin Friday.[6]
Military
Saint Vincent has no formal armed forces, although the Royal Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Police Force includes a Special Service Unit as well as a militia that has a supporting role on the island.
In 2017, Saint Vincent signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.[28]
Administrative divisions
Administratively, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is divided into six parishes. Five parishes are on Saint Vincent, while the sixth is made up of the Grenadine islands. Kingstown is located in the Parish of Saint George and is the capital city and central administrative centre of the country.[6]
LGBT rights
Acts of gross indecency, which may be defined to include homosexual activity, are illegal in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.[29] Section 148 of the Criminal Code states:
Any person, who in public or private, commits an act of gross indecency with another person of the same sex, or procures or attempts to procure another person of the same sex to commit an act of gross indecency with him or her, is guilty of an offence and liable to imprisonment for five years.[30]
Foreign relations
International and regional relationships
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines maintains close ties to Canada, the United Kingdom and the US, and cooperates with regional political and economic organisations such as the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS) and CARICOM.[31] The island nation's sixth embassy overseas was opened on 8 August 2019 in Taipei, after Prime Minister Ralph Gonsalves' official visit to the Republic of China; the other five are located in London, Washington D.C., Havana, Caracas and Brussels.
The Double Taxation Relief (CARICOM) Treaty
On 6 July 1994 at Sherbourne Conference Centre, St Michael, Barbados, as a representative of the Government of St. Vincent and the Grenadines, then (James Mitchell, who was subsequently knighted) signed the Double Taxation Relief (CARICOM) Treaties.[31] There were seven other signatories to the agreement on that day. The countries which were represented were Antigua and Barbuda, Belize, Grenada, Jamaica, St Kitts and Nevis, St Lucia, and Trinidad and Tobago.
An eighth country signed the agreement on 19 August 2016, Guyana.
This treaty covered taxes, residence, tax jurisdictions, capital gains, business profits, interest, dividends, royalties and other areas.[31]
FATCA
On 30 June 2014, St. Vincent and the Grenadines signed a Model 1 agreement with the United States of America with respect to Foreign Account Tax Compliance (Act) or FATCA.[32]
According to the updated site as of 16 January 2017, on 13 May 2016 the agreement went to "In Force" status.
International and regional bodies to which St. Vincent and the Grenadines belong
St Vincent and the Grenadines is a member of the United Nations, the Commonwealth of Nations, the Organization of American States, and the Association of Caribbean States (ACS).
In September 2017, at the 72nd Session of the UN General Assembly, the Prime Ministers of the Solomon Islands, Tuvalu, Vanuatu and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines called for UN action on alleged human rights abuses committed on Western New Guinea's indigenous Papuans.[33] Western New Guinea has been occupied by Indonesia since 1963.[34] More than 100,000 Papuans have died during a 50-year Papua conflict.[35]
Organisation of American States
The Charter of the OAS was signed in Bogotá in 1948 and was amended by several Protocols which were named after the city and the year in which the Protocol was signed, such as "Managua" in "1993" forming part of the name of the Protocol.[36]
St Vincent and the Grenadines entered the OAS system on 27 October 1981 according to the OAS website.[37]
Summits of the Americas
The last Summits of the Americas, the seventh, was held in Panama City, Panama in 2015 with the eighth summit being held in Lima, Peru in 2018 according to the website of the Summits of Americas.[38]
Indigenous Leaders Summits of Americas (ILSA)
With St Vincent and the Grenadines having at least two groups of indigenous persons[39] it is expected that there will be contributions from the SVG's on this topic at the next ILSAs.[40]
The position of the OAS with respect to indigenous persons appears to be developing over the years. The following statements appear to capture the position of the OAS with respect to the ILSA: "The OAS has supported and participated in the organisation of Indigenous Leaders Summits of Americas (ILSA)" according to the OAS's website. The most recent "statement made by the Heads of State of the hemisphere was in the Declaration of Commitments of Port of Spain in 2009 – Paragraph 86 according to the OAS's website."[41]
The Draft American Declaration of the Rights of the Indigenous Persons appear to be a working document. The last "Meeting for Negotiations in the Quest for Consensus on this area appeared to be Meeting Number (18) eighteen and is listed as being held in May 2015 according to the website."[42]
European nations
In 2013, Saint Vincent called for European nations to pay reparations for the slave trade.[43]
Venezuela
Saint Vincent protests against Venezuela's claim to give full effect to Aves (Bird) Island, which creates a Venezuelan EEZ/continental shelf extending over a large portion of the Caribbean Sea.[6]
Economy
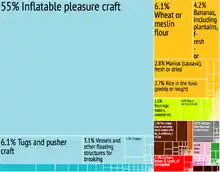

Agriculture, dominated by banana production, is the most important sector of this lower-middle-income economy. The services sector, based mostly on a growing tourist industry, is also important. The government has been relatively unsuccessful at introducing new industries, and the unemployment rate remains high at 19.8% in the 1991 census[44] to 15% in 2001.[45] The continuing dependence on a single crop represents the biggest obstacle to the islands' development as tropical storms wiped out substantial portions of bananas in many years.
There is a small manufacturing sector and a small offshore financial sector serving international businesses, and its secrecy laws have caused some international concern. There are increasing demands for international financial services like stock exchange and financial intermediaries financial activities in the country. In addition, the natives of Bequia are permitted to hunt up to four humpback whales per year under IWC subsistence quotas.
Tourism
The tourism sector has considerable potential for development. The recent filming of the Pirates of the Caribbean movies on the island has helped to expose the country to more potential visitors and investors. Recent growth has been stimulated by strong activity in the construction sector and an improvement in tourism.[46]
Transportation
Argyle International Airport is the country's new international airport.[47] The new facility opened on 14 February 2017,[48] replacing the existing E.T. Joshua Airport. The airport is on the island's east coast about 8.3 km (5.17 miles) from Kingstown.
Communications
In 2010, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines had 21,700 telephone land lines. Its land telephone system is fully automatic and covers the entire island and all of the inhabited Grenadine islands.[45] In 2002, there were 10,000 mobile phones.[49] By 2010, this number had increased to 131,800.[45] Mobile phone service is available in most areas of Saint Vincent as well as the Grenadines.
Saint Vincent has two ISPs (Digicel, Flow) that provide cellular telephone and internet service.[50]
Demographics
The population as estimated in 2018 was 110,211.[2][3] The ethnic composition was 66% African descent, 19% of mixed descent, 6% East Indian, 4% Europeans (mainly Portuguese), 2% Island Carib and 3% others.[6] Most Vincentians are the descendants of African people brought to the island to work on plantations. There are other ethnic groups such as Portuguese (from Madeira) and East Indians, both brought in to work on the plantations after the abolishing of slavery by the British living on the island. There is also a growing Chinese population.
Languages
English is the official language. Most Vincentians speak Vincentian Creole.[51] English is used in education, government, religion, and other formal domains, while Creole (or 'dialect' as it is referred to locally) is used in informal situations such as in the home and among friends.[52]
Religion

According to the 2001 census, 81.5% of the population of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines identified themselves as Christian, 6.7% has another religion and 8.8% has no religion or did not state a religion (1.5%).[53]
Anglicanism constitutes the largest religious category, with 17.8% of the population. Pentecostals are the second largest group (17.6%). The next largest group are Methodists (10.9% of the population), followed by Seventh-day Adventists (10.2%) and Baptists (10.0%). Other Christians include Jehovah's Witnesses (0.6%), Roman Catholics (7.5%), Evangelicals (2.8%), Church of God (2.5%), Brethren Christian (1.3%), and the Salvation Army (0.3%).[54]
Between 1991 and 2001 the number of Anglicans, Brethren, Methodists and Roman Catholics decreased, while the number of Pentecostals, Evangelicals and Seventh-day Adventists increased.
The number of non-Christians is small. These religious groups include the Rastafarians (1.5% of the population), Hindus and Muslims (1.5%).[55]
Culture

Sport
Cricket, rugby and association football are most popular among men whereas netball is most popular among women. Basketball, volleyball and tennis are also very popular.[56]
The country's prime football league is the NLA Premier League, which provides its national (association) football team with most players. A notable Vincentian footballer is Ezra Hendrickson, former national team captain who played at several Major League Soccer clubs in the United States and is now an assistant coach with the Seattle Sounders FC.[57]
The country regularly participates at the Caribbean Basketball Championship where a men's team and a women's team compete. Saint Vincent and the Grenadines also has its own national rugby union team which is ranked 84th in the world. Other notable sports played at the regional level include track and field.
Music
Music popular in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines includes big drum, calypso, soca, steelpan and reggae. String band music, quadrille and traditional storytelling are also popular. One of the most successful St Vincent natives is Kevin Lyttle. He was named Cultural Ambassador for the Island 19 September 2013.[58]
The national anthem of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is "Saint Vincent, Land so beautiful", adopted upon independence in 1979.
Media
Saint Vincent has twelve FM radio stations: 88.9 Adoration Fm,[59] 89.1 Jem Radio, 89.7 NBC Radio, 95.7 and 105.7 Praise FM, 96.7 Nice Radio, 97.1 Hot 97, 98.3 Star FM, 99.9 We FM, 103.7 Hitz, 102.7 EZee radio, 104.3 Xtreme FM and 106.9 Boom FM. There are several Internet radio stations including Chronicles Christian Radio.[60] It has one television broadcast station ZBG-TV (SVGTV)[61] and one cable television provider.
St Vincent and the Grenadines Broadcasting Co-operation is the parent company for SVGTV, Magic 103.7.[62]
See also
References
- "Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Demographics Profile". Index Mundi. Retrieved 12 December 2020.
- ""World Population prospects – Population division"". population.un.org. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 9 November 2019.
- ""Overall total population" – World Population Prospects: The 2019 Revision" (xslx). population.un.org (custom data acquired via website). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 9 November 2019.
- Report on St. Vincent and the Grenadines, International Monetary Fund.
- Human Development Report 2020 The Next Frontier: Human Development and the Anthropocene (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 15 December 2020. pp. 343–346. ISBN 978-92-1-126442-5. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "CIA World Factbook – St Vincent". Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- "The Commonwealth – St Vincent and the Grenadines". Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- "The Commonwealth – St Vincent and the Grenadines". Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- Yurumein (Homeland): A Documentary on Caribs in St. Vincent
- Frere. Adrien Le Breton SJ. (1662–1736). Historic Account of Saint Vincent, the Carib Youroumayn, the island of the Karaÿbes. Paris: Museum of Natural History, Fonds Jussieu.
- David Lawrence Niddrie, Richard Tolson, Adrian Fraser (21 October 2019). "Saint Vincent and the Grenadines". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 7 July 2019.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "St Vincent Genealogy Resources". svgancestry.com. Archived from the original on 21 March 2012.
- Pyle, David. "A volcanic retrospective: eruptions of the Soufrière, St Vincent". Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- corporateName=Commonwealth Parliament; address=Parliament House, Canberra. "Sir David Smith "An Australian Head of State: An Historical and Contemporary Perspective [1]"". www.aph.gov.au. Retrieved 12 August 2020.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "St. Vincent Suppresses Short‐Lived Rebellion On Isle in Grenadines". Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- "Union remembers December 7 uprising". Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 6 October 2011. Retrieved 12 September 2011.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- St Vincent and the Grenadines profile – Leaders, BBC News (27 November 2014).
- Ralph E. Gonsalves, The Making of "The Comrade": The Political Journey of Ralph Gonsalves: an Autobiographical Sketch of a Caribbean Prime Minister (SFI Books, 2010).
- "Caribbean nations consider push for slavery reparations". Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- St Vincent and the Grenadines country profile, BBC News (31 May 2018).
- "Constitutional reform referendum defeated in St Vincent & the Grenadines". Antillean. 26 November 2009. Archived from the original on 18 February 2010. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- Balboni, Julien (10 October 2018). "L'enfer d'une société belge au paradis terrestre". L'Echo (in French). Archived from the original on 8 January 2019. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568.
- Grantham, H. S.; et al. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity - Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1). doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723.
- "SVG's First Female Head of State Sworn In". Searchlight.vc. 1 August 2019. Retrieved 23 August 2019.
- Profile Archived 6 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine, caribbeanelections.com; accessed 1 September 2014.
- "Chapter XXVI: Disarmament – No. 9 Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons". United Nations Treaty Collection. 7 July 2017.
- Avery, Daniel (4 April 2019). "71 Countries Where Homosexuality is Illegal". Newsweek.
- United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. "Saint Vincent and the Grenadines: Situation and treatment of homosexuals; legislation; availability of state protection and support services (2007 – September 2009)". Refworld. Archived from the original on 28 July 2011.
- "The Double Taxation Relief (Caricom) Order" (PDF). Legal Supplement. 33 (273). 28 December 1994.
- "Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA)". Treasury.gov. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- "Fiery debate over West Papua at UN General Assembly". Radio New Zealand 2017. 27 September 2017.
- "Freedom of the press in Indonesian-occupied West Papua". The Guardian. 22 July 2019.
- "Goodbye Indonesia". Al-Jazeera. 31 January 2013.
- "Charter of the Organization of American States". Organization of American States. 1 August 2009. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- "Member State: Saint Vincent and the Grenadines". Organization of American States. 1 August 2009. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- "Home". Summits of the Americas. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- "World Directory of Minorities and Indigenous Peoples – St Vincent and the Grenadines". United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- "Indigenous Peoples". Organization of American States. 1 August 2009. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- "Indigenous Peoples". Summits of The Americas. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- "Events OAS Indigenous Special Events". Organization of American States. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- "Caribbean leaders make case for reparations at U.N." The Miami Herald. 29 September 2013.
- "Statement of St Vincent & the Grenadines". United Nations Population Information Network. 9 September 1994. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- "The World Fact Book". Central Intelligence Agency. 10 November 2011. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- Culzac-Wilson, Lystra (October 2003). "Report to the Regional Consultation on SIDS Specific Issues" (PDF). United Nations Environment Program. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- "Argyle International Airport, St Vincent & the Grenadines". caribbeanconstruction.com. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- "Argyle International Airport to open February 14". Antigua Observer Newspaper. 29 December 2016. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
- "Saint Vincent and the Grenadines". About.com. 1 November 2005. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- "About SVG: Essentials". SVG Tourism Authority. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- "Vincentian Creole English". Ethnologue. 19 February 1999. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- "The Classification of the English-Lexifier Creole Languages Spoken in Grenada, Guyana, St Vincent, and Tobago Using a Comparison of the Markers of Some Key Grammatical Features". SIL International. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- "Population and housing census report 2001". stats.gov.vc. Archived from the original on 11 September 2018. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- Sen Nag, Oishimaya (13 November 2018). "Religious Beliefs In Saint Vincent and the Grenadines". World Atlas.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 August 2011. Retrieved 27 November 2010.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Visit St Vincent & the Grenadines – Sport". visitsvg.com. Archived from the original on 19 September 2015. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
- "Ezra Hendrickson, Assistant Coach". Seattle Sounders FC. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- "Kevin Lyttle, "Skinny Fabulous," n "Fireman Hooper" Are Named Cultural Ambassadors". Islandmix.com. 19 September 2013. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- "Contemporary Christian Radio Station". Adoration FM SVG. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- "About Caribbean Christian Radio Online". Chronicles Christian Radio. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- "SVGTV". St Vincent and the Grenadines Broadcasting Corporation Ltd. Archived from the original on 8 January 2012. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- "Welcome to the Saint Vincent & The Grenadines Broadcasting Corporation Website". SVGBC. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
Further reading
- Bobrow, Jill & Jinkins, Dana. 1985. St. Vincent and the Grenadines. 4th Edition Revised and Updated, Concepts Publishing Co., Waitsfield, Vermont, 1993.
- Cosover, Mary Jo. 1989. "St. Vincent and the Grenadines." In Islands of the Commonwealth Caribbean: A Regional Study, edited by Sandra W. Meditz and Dennis M. Hanratty. US Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C.
- CIA Factbook entry
- Gonsalves, Ralph E. 1994. History and the Future: A Caribbean Perspective. Quik-Print, Kingstown, St Vincent.
- US Dept of State Profile
- Williams, Eric. 1964. British Historians and the West Indies, Port-of-Spain.
External links
- Government
- Official website
- Website of the Prime Minister of St Vincent and the Grenadines
- Chief of State and Cabinet Members
- General information
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines at Curlie
- St Vincent and the Grenadines from the BBC News
 Wikimedia Atlas of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Wikimedia Atlas of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines- Key Development Forecasts for St Vincent and the Grenadines from International Futures
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Private Sector Assessment Report