Scheduled Banks (India)
Scheduled Banks in India refer to those banks which have been included in the Second Schedule of Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. RBI in turn includes only those banks in this Schedule which satisfy the criteria laid down vide section 42(6)(a) of the said Act. Banks not under this Schedule are called Non-Scheduled Banks
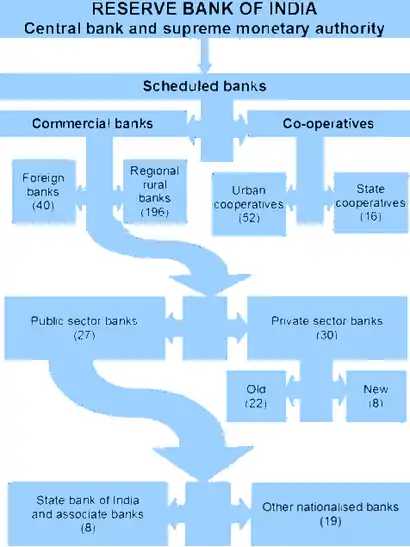
Structure of the organised banking sector in India.
Facilities
Every Scheduled bank enjoys two types of principal facilities: it becomes eligible for debts/loans at the bank rate from the RBI; and, it automatically acquires the membership of clearing house.[1]
Types of banks
There are two main categories of commercial banks in India namely -
- Scheduled Commercial banks
- Scheduled Co-operative banks
Scheduled commercial Banks are further divided into 5 types as below -
- Nationalised Banks
- Development Banks
- Regional Rural Banks
- Foreign Banks
- Private sector Banks
Scheduled Co-operative banks are further divided into 2 types namely -
- Scheduled State Co-operative banks
- Scheduled Urban Co-operative banks
See also
References
- "Bharatiya Mahila Bank included in second schedule to RBI Act". Live Mint. 21 May 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
Further reading
- "Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934: The Second Schedule" (PDF). Reserve Bank of India. p. 91-100.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.