Schoenocaulon officinale
Schoenocaulon officinale, called sabadilla, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Schoenocaulon, native to Mexico, Central America, and Venezuela.[2] It is highly toxic, containing veratridine, cevadine, and other alkaloids. Its seeds were used by pharmacists around the world to prepare delousing solutions and insecticides. It is still collected and used locally to rid domestic animals of fleas, ticks, lice and other parasites, and attempts are being made to revive the industry.[3]
| Schoenocaulon officinale | |
|---|---|
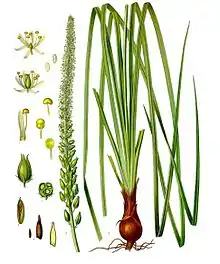 | |
| Botanical illustration | |
 | |
| Seeds | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Liliales |
| Family: | Melanthiaceae |
| Genus: | Schoenocaulon |
| Species: | S. officinale |
| Binomial name | |
| Schoenocaulon officinale | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
List
| |
References
- G.Bentham, Pl. Hartw.: 29 (1840)
- "Schoenocaulon officinale (Schltdl. & Cham.) A.Gray". Plants of the World Online. Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 2017. Retrieved 31 December 2020.
- Hare, J. Daniel (1996). "Purification and Quantitative Analysis of Veratridine and Cevadine by HPLC". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 44: 149–152. doi:10.1021/jf9406828.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.