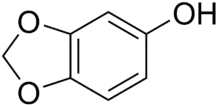
Sesamol
Sesamol is a natural organic compound which is a component of sesame seeds and sesame oil. It is a white crystalline solid that is a derivative of phenol. It is sparingly soluble in water, but miscible with most oils. It can be produced by organic synthesis from heliotropine.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-ol | |
| Other names
1,3-Benzodioxol-5-ol Benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ol Sesamol 3,4-Methylenedioxyphenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.784 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 138.12 g/mol |
| Melting point | 62 to 65 °C (144 to 149 °F; 335 to 338 K) |
| Boiling point | 121 to 127 °C (250 to 261 °F; 394 to 400 K) at 5 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sesamol has been found to be an antioxidant that may prevent the spoilage of oils.[2][3] It also may prevent the spoilage of oils by acting as an antifungal.[4]
Sesame oil is used in Ayurvedic Medicine.[5]
It can be used in the synthesis of paroxetine.[6]:138–141
Alexander Shulgin used sesamol in his book PiHKAL to make MMDA-2.
References
- Sesamol Archived 2010-01-14 at the Wayback Machine at Chemicalland21.com
- Joo Yeon Kim, Dong Seong Choi and Mun Yhung Jung "Antiphoto-oxidative Activity of Sesamol in Methylene Blue- and Chlorophyll-Sensitized Photo-oxidation of Oil" J. Agric. Food Chem., 51 (11), 3460 -3465, 2003.
- Ohsawa, Toshiko. "Sesamol and sesaminol as antioxidants." New Food Industry (1991), 33(6), 1-5.
- Wynn, James P.; Kendrick, Andrew; Ratledge, Colin. "Sesamol as an inhibitor of growth and lipid metabolism in Mucor circinelloides via its action on malic enzyme." Lipids (1997), 32(6), 605-610.
- "A Closer Look at Ayurvedic Medicine". Focus on Complementary and Alternative Medicine. Bethesda, Maryland: National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM), US National Institutes of Health (NIH). 12 (4). Fall 2005 – Winter 2006. Archived from the original on 2006-12-09.
- Li, Jie Jack (2004). Contemporary drug synthesis. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-21480-9.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
