Sims' position
The Sims position, named after the gynaecologist J. Marion Sims, is usually used for rectal examination, treatments, enemas, and examining women for vaginal wall prolapse.[1][2]

Posterior view of the Sims' position
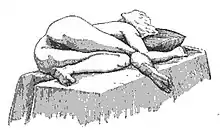
Anterior view of the Sims' position
It is performed by having the person lie on their left side, left hip and lower extremity straight, and right hip and knee bent. It is also called lateral recumbent position.[3] The Sims position is also described with the person lying on their left side with both legs bent.[4]
Detailed description
The position is described as follows:
- Patient lies on their left side.
- Patient's left lower extremity is straightened.
- Patient's right lower extremity is flexed at the hip, and the leg is flexed at the knee. The bent knee, resting against bed surface or a pillow, provides stability.[5]
Common uses:
- Administering enemas
- Postpartum perineal examination
- Per-rectal examination
- Osteopathic manipulative treatment techniques
See also
References
- Pamela J. Carter; Susan Lewsen (2005). "11. Positioning, lifting, and transferring patients and residents". Lippincott's Textbook for Nursing Assistants: A Humanistic Approach to Caregiving. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 188. ISBN 978-0-7817-3981-8.
- Naftalin, Alan (2012). "4. Women". In Michael Glynn (ed.). Hutchison's Clinical Methods : An Integrated Approach to Clinical Practice, 23/e. Elsevier. p. 47. ISBN 978-81-312-3288-0.
- "Sim's position : Definition". The Free Medical Dictionary. Retrieved 27 August 2012.
- Bendon, C.; Price, N. (2011). "Sims Speculum Examination". www.semanticscholar.org. Retrieved 17 October 2020.
- "Patient positioning : Sim's position". MoonDragon. Archived from the original on 25 August 2012. Retrieved 27 August 2012.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.