Sinhc function
In mathematics, the Sinhc function appears frequently in papers about optical scattering,[1] Heisenberg Spacetime[2] and hyperbolic geometry.[3] It is defined as[4][5]
It is a solution of the following differential equation:
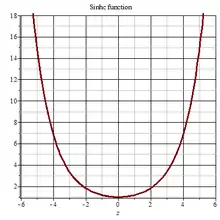
Sinhc 2D plot
_2D_plot.png.webp)
Sinhc'(z) 2D plot
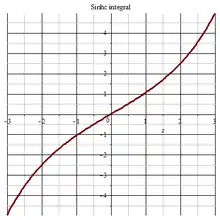
Sinhc integral 2D plot
- Imaginary part in complex plane
- Real part in complex plane
- absolute magnitude
- First-order derivative
- Real part of derivative
- Imaginary part of derivative
- absolute value of derivative
In terms of other special functions
Series expansion
Padé approximation
Gallery
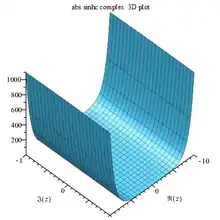 Sinhc abs complex 3D |
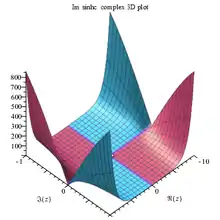 Sinhc Im complex 3D plot |
 Sinhc Re complex 3D plot |
_Im_complex_3D_plot.png.webp) Sinhc'(z) Im complex 3D plot |
_Re_complex_3D_plot.png.webp) Sinhc'(z) Re complex 3D plot |
_abs_complex_3D_plot.png.webp) Sinhc'(z) abs complex 3D plot |
 Sinhc abs plot |
 Sinhc Im plot |
 Sinhc Re plot |
_Im_plot.JPG.webp) Sinhc'(z) Im plot |
_abs_plot.JPG.webp) Sinhc'(z) abs plot |
_Re_plot.JPG.webp) Sinhc'(z) Re plot |
References
- PN Den Outer, TM Nieuwenhuizen, A Lagendijk, Location of objects in multiple-scattering media, JOSA A, Vol. 10, Issue 6, pp. 1209–1218 (1993)
- T Körpinar, New characterizations for minimizing energy of biharmonic particles in Heisenberg spacetime - International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 2014 - Springer
- Nilg¨un S¨onmez, A Trigonometric Proof of the Euler Theorem in Hyperbolic Geometry, International Mathematical Forum, 4, 2009, no. 38, 1877–1881
- JHM ten Thije Boonkkamp, J van Dijk, L Liu, Extension of the complete flux scheme to systems of conservation laws, J Sci Comput (2012) 53:552–568, DOI 10.1007/s10915-012-9588-5
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Sinhc Function." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/SinhcFunction.html
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.