Spirodiclofen
Spirodiclofen is an acaricide and insecticide used in agriculture to control mites and San Jose scale. In the United States, it is used on citrus, grapes, pome fruit, stone fruit, and tree nut crops.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
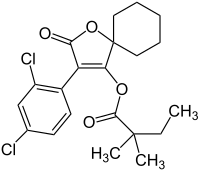
| IUPAC name
3-(3,5-Dichlorophenyl)-2-oxo-1-oxaspiro[4.5]dec-3-en-4-yl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.130.204 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H24Cl2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 411.32 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 94.8 °C (202.6 °F; 367.9 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H317, H350, H361, H373, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P272, P273, P280, P281, P302+352, P308+313, P314, P321, P333+313, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Spirodiclofen belongs to the tetronic acid class and acts by inhibiting lipid biosynthesis.[3]
References
- "EPA Pesticide Fact Sheet: Spirodiclofen" (PDF). Environmental Protection Agency.
- "Spirodiclofen" (PDF). Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations.
- De Maeyer, L; Geerinck, R (2009). "The multiple target use of spirodiclofen (Envidor 240 SC) in IPM pomefruit in Belgium". Communications in Agricultural and Applied Biological Sciences. 74 (1): 225–32. PMID 20218531.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.