St Stephen's Green
St Stephen's Green (Irish: Faiche Stiabhna)[1] is a public park located in the city centre of Dublin, Ireland. The current landscape of the park was designed by William Sheppard. It was officially re-opened to the public on Tuesday, 27 July 1880 by Lord Ardilaun.[2][3] The park is adjacent to one of Dublin's main shopping streets, Grafton Street, and to a shopping centre named after it, while on its surrounding streets are the offices of a number of public bodies as well as a stop on one of Dublin's Luas tram lines. It is often informally called Stephen's Green. At 22 acres (8.9 ha), it is the largest of the parks in Dublin's main Georgian garden squares. Others include nearby Merrion Square and Fitzwilliam Square.
| St Stephen's Green | |
|---|---|
 Aerial view of St Stephen’s Green | |
 St Stephen's Green  St Stephen's Green  St Stephen's Green | |
| Type | City park |
| Location | Dublin, Ireland |
| Coordinates | 53°20′17″N 6°15′33″W |
| Area | 8.9 ha (22 acres) |
| Created | 1664 |
| Operated by | Office of Public Works |
| Status | Open all year |
| Public transit access | St Stephen's Green station |
| Website | ststephensgreenpark.ie |
The park is rectangular, surrounded by streets that once formed major traffic arteries through Dublin city centre, although traffic management changes implemented in 2004 during the course of the Luas works[4] have greatly reduced the volume of traffic. These four bordering streets are called, respectively, St Stephen's Green North, St Stephen's Green South, St Stephen's Green East and St Stephen's Green West.
History

.jpg.webp)
Until 1663 St Stephen's Green was a marshy common on the edge of Dublin, used for grazing. In that year Dublin Corporation, seeing an opportunity to raise much-needed revenue, decided to enclose the centre of the common and to sell land around the perimeter for building.[5] The park was enclosed with a wall in 1664. The houses built around the Green were rapidly replaced by new buildings in the Georgian style and by the end of the eighteenth century the Green was a place of resort for the better-off of the city. Most of the present-day landscape of the square comprises townhouses from the 18th and 19th centuries.[6]

In 1814 control of St Stephen's Green passed to Commissioners for the local householders, who redesigned its layout and replaced the walls with railings.[7]
After the death of Prince Albert, Queen Victoria suggested that St Stephen's Green be renamed Albert Green and have a statue of Albert at its centre, a suggestion rejected with indignation by the Dublin Corporation and the people of the city, to the Queen's chagrin.[8]
Access to the Green was restricted to local residents, until 1877, when Parliament passed an Act to reopen St Stephen's Green to the public, at the initiative of Sir A.E. Guinness, a member of the Guinness brewing family who lived at St Anne's Park, Raheny and at Ashford Castle. He later paid for the laying out of the Green in approximately its current form, which took place in 1880, and gave it to the Corporation, as representatives of the people. By way of thanks, the city commissioned a statue of him, which faces the College of Surgeons. His brother Edward lived at Iveagh House, which his descendants gave in 1939 to the Department of External Affairs (now the Department of Foreign Affairs).
During the Easter Rising of 1916, a group of insurgents made up mainly of members of the Irish Citizen Army, under the command of Commandant Michael Mallin, his second-in-command Kit Poole, and Constance Markievicz, established a position in St Stephen's Green.[5] They numbered between 200 and 250.[9] They confiscated motor vehicles to establish roadblocks on the streets that surround the park, and dug defensive positions in the park itself. This approach differed from that of taking up positions in buildings, adopted elsewhere in the city. It proved to have been unwise when elements of the British Army took up positions in the Shelbourne Hotel, at the northeastern corner of St Stephen's Green, overlooking the park, from which they could shoot down into the entrenchments.[5] Finding themselves in a weak position, the Volunteers withdrew to the Royal College of Surgeons on the west side of the Green.[9] During the Rising, fire was temporarily halted to allow the park's groundsman to feed the local ducks.[10]
The park is now operated by the Office of Public Works (OPW) on behalf of the Irish state.[11]
Evolution of design
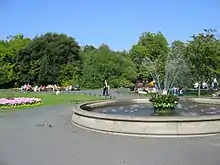
The landscaping of the park has undergone three major changes since its inception. Its first major change occurred in 1670: two rows of lime trees were planted around the perimeter, functioning as its first enclosure. At this time, the park was only accessible to the wealthy residents who owned plots around the park.[2]
In 1815 the park was redesigned by the Dublin city surveyor Arthur Neville. In his redesign, he added winding pathways and iron fences. At this time, the park was still closed to the public.[2]
During the 1860s, the campaign to make the park publicly accessible was underway, and the city engineer, George W. Hemans,[12] proposed a new design to make the park as walkable and as functionally practical as possible. This included creating four gates at each corner of the park that would be linked by the extant pathways designed by Neville. This plan was eventually abandoned, most likely due to the fact that Hemans was employed by Dublin Corporation. However, many of Hemans' designs, like the addition of the gates and connecting pathways, were included in the final plans submitted by William Sheppard, the principal designer responsible for the landscape of the park as we know it today, and engineer A.L. Cousins, sponsored by Lord Ardilaun. Ardilaun also played a significant role in the planning and importing of the exotic trees and plants that would be installed in the park.[2]
Park layout



While the central park of St Stephen's Green is one of three ancient commons in the city, its current layout owes much to the restorations of the 1800s (see History above).
The grounds are roughly rectangular, measuring (approximately) 550 by 450 metres, and are centred on a formal garden.

One of the more unusual aspects of the park lies on the north-west corner of this central area, a garden for the blind with scented plants, which can withstand handling, and are labelled in Braille.
Further north again (and spanning much of the length of the park) is a large lake. Home to ducks and other water fowl, the lake is fed by an artificial waterfall, spanned by O'Connell bridge, and fronted by an ornamental gazebo. The lakes in the park are fed from the Grand Canal at Portobello.
To the south side of the main garden circle is more open heath surrounding a bandstand, and often frequented by lunching students, workers and shoppers on Dublin's sunnier days.
There is also a playground (separated into junior and senior areas) which was refurbished in 2010.
The park once featured a statue of King George II on horseback (erected in 1758) until it was blown up in 1937 by Irish Republicans, the day after the coronation of George VI.[13][14]
Other notable features include:
- the Fusiliers' Arch at the Grafton Street corner which commemorates the Royal Dublin Fusiliers who died in the Second Boer War.
- a fountain representing the Three Fates inside the Leeson Street gate. The statue was designed by Joseph Wackerle in bronze in 1956. It was a gift from the German people in thanks for Irish help to refugee children following World War II. Up to five hundred children found foster-homes in Ireland in a project named Operation Shamrock.
- a seated statue of Lord Ardilaun on the western side, the man who gave the Green to the city, facing the Royal College of Surgeons which he also sponsored (again, see History above)
- the Yeats memorial garden with a sculpture by Henry Moore
- a bust of James Joyce facing his former university at Newman House
- a memorial to the Fenian leader Jeremiah O'Donovan Rossa near the Grafton Street entrance
- a bronze statue at the Merrion Row corner of Theobald Wolfe Tone, the leader of the 1798 rebellion.
- a memorial to the Great Famine of 1845–1850 by Edward Delaney
- a bust of Constance Markievicz on the south of the central garden (see History above)
- a statue of Robert Emmet standing opposite his birthplace (now demolished) at No 124.
- a memorial bust of Thomas Kettle, fatality of the Great War. The attempt to erect a commemorative portrait bust of Kettle was beset by controversy until it was finally placed, without official unveiling, in the centre section.
Notable addresses

Iveagh House on the south side was created from the joining of two earlier houses (numbers 80 and 81) by Benjamin Guinness in the 1860s. It was donated to the Irish State by the Guinness family in 1939, and now houses the main offices of the Department of Foreign Affairs.
Also on the south side of St Stephen's Green are Newman House (numbers 85 and 86, after John Henry Newman) and University Church. These are home to the Catholic University of Ireland, which was founded in the 19th Century. It is linked with University College Dublin, but is no longer active educationally in its own right.
The Unitarian Church, Dublin, built in the Gothic revival style, is located on the West side of St Stephen's Green.
Also on the west side is the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland (number 123), home to the oldest of the Republic of Ireland's six medical schools.
On the west side, at the top of Grafton Street, is the Stephen's Green Shopping Centre, built in October 1988. It was, at the time, Ireland's largest shopping centre. Its style was intended to represent a conservatory on the side facing the Green and to mirror the brickwork design of the opposing Gaiety Theatre on South King Street.
On the north side of St Stephen's Green, there were four[5] but are now two clubs (originally gentlemen's clubs): the Hibernian United Services Club (number 8, closed in 2002), the Stephen's Green Hibernian Club (number 9, originally the Stephen's Green Club, prior to its merger with the Hibernian United Services Club), the "Friendly Brothers of St Patrick" (number 22, now closed) and the Kildare Street and University Club (number 17). This side of the Green also has the historic Shelbourne Hotel and the Little Museum of Dublin, which is housed in a restored Georgian townhouse.
Also on the north side, Heritage House at 23 St Stephen's Green, was the location of a tearoom which hosted the first public Alcoholics Anonymous meeting in Ireland, on 25 November 1946.[15][16]
Loreto College, St Stephen's Green, one of Ireland's best-known fee-paying schools for girls, is located at number 53, on the East side of the Green.
St Vincent's Hospital, now located in a suburb on the south side of Dublin, was formerly located in buildings on the East side of St Stephen's Green and on Leeson Street.
Transport
Dublin Bus routes 7b, 7d, 11, 32x, 37, 41x, 44, 46a, 61, 84x, 145, 155 and 757 all have stops along the east side of the square
The Green line of the Luas tram system stops at the St Stephen's Green stop on the western side of the park, with Luas Cross City services continuing to Broombridge station in Cabra.[17][18]
Notes
- "Sraidainmneacha Bhaile Atha Cliath" (PDF). Dublin City Council. Retrieved 30 November 2014.
- "Report on St Stephen's Green" (PDF). UCD School of Archaeology.
- "Heritage Ireland: St Stephens Green". www.heritageireland.ie. Archived from the original on 1 December 2014. Retrieved 25 September 2017.
- "Roadworks on St Stephen's Green to reverse traffic flow and restrict movement". The Irish Times. 6 June 2004. Archived from the original on 20 May 2011. Retrieved 30 November 2014.
- Casey, Christine (2006). Dublin: The City Within the Grand and Royal Canals and the Circular Road with the Phoenix Park. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-10923-8.
- "National Inventory of Architectural Heritage".
- "Archiseek.com – St Stephen's Green, Dublin". Archiseek.com. Archived from the original on 11 January 2008.
- "A queen's welcome: Victoria's stormy affair with Ireland". Irish Examiner. 26 June 2010.
- "The 1916 Rising: Personalities and Perspectives – Stephens Green" (PDF). National Library of Ireland. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 November 2015. Retrieved 30 November 2014.
- Michael O'Sullivan, Bernard O'Neill: The Shelbourne and its people (Blackwater Press 1999), p.45 ISBN 1-84131-442-0
- "OPW Heritage Ireland Site – St Stephens Green page". HeritageIreland.ie (OPW). Archived from the original on 1 December 2014. Retrieved 30 November 2014.
- "Dictionary of Irish Architects - HEMANS, GEORGE WILLOUGHBY". Dia.ie. 13 November 1926. Retrieved 28 December 2013.
- Carpenter, Andrew, ed. (1998). Verse in English from Eighteenth-century Ireland. Cork University Press. ISBN 9781859181034.
- Chastel-Rousseau, Charlotte, ed. (2011). Reading the Royal Monument in Eighteenth-century Europe. Ashgate Publishing. ISBN 9780754655756.
- "A Catholic Members Appreciation". Furrow Magazine. November 1953 – via a-1associates.com.
- "News Sheet" (PDF). alcoholicsanonymous.ie. October 2016. Retrieved 15 December 2020.
- "Green light given to Luas link-up, first passengers 2017 – RTÉ News". Rte.ie. 3 August 2012. Archived from the original on 5 August 2012. Retrieved 30 August 2012.
- "Taoiseach launches new Luas Cross City service in Dublin". RTÉ. 9 December 2017. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to St. Stephen's Green. |