Stagnicola palustris
Stagnicola palustris is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Lymnaeidae, the pond snails.
| Stagnicola palustris | |
|---|---|
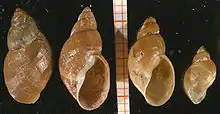 | |
| Four shells of Stagnicola palustris | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| (unranked): | |
| Superfamily: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | Lymnaeinae |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | S. palustris |
| Binomial name | |
| Stagnicola palustris (O. F. Müller, 1774)[2] | |
| Synonyms[3][4] | |
| |
_-_Lymnaeidae_-_Mollusc_shell.jpeg.webp)
Stagnicola palustris (Müller, 1774), museum specimens Naturalis
Taxonomy
Stagnicola turricula is a synonym of Stagnicola palustris, because they are not genetically independent,[5] but S. curricula is still sometimes listed separately.[6][7]
Description
The dimensions of the shell of an adult of this species are from about 10 to 18 mm in length, and about 6 to 10 mm in width.[8]
Distribution
This species of snail occurs in European countries and islands including:
- Croatia
- Stagnicola palustris – Czech Republic[5] – data deficient (DD)[9]
- Germany – (Arten der Vorwarnliste)[10]
- Great Britain
- Netherlands
- Poland
- Slovakia[5]
Habitat
This snail lives in shallow, well-aerated freshwater habitats.
See also
Stagnicola palustris-like snails in the North America are named Stagnicola elodes, but that may be the same species.[11]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Stagnicola palustris. |
References
- von Proschwitz T. & García N. (2012). "Stagnicola palustris". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2014.2. <www.iucnredlist.org>. Downloaded on 03 September 2014.
- Müller O. F. (1774). Vermivm terrestrium et fluviatilium, seu animalium infusoriorum, helminthicorum, et testaceorum, non marinorum, succincta historia. Volumen alterum. pp. I-XXVI [= 1–36], 1–214, [1–10]. Havniae & Lipsiae. (Heineck & Faber).
- Bargues M. D., Vigo M., Horak P., Dvorak J., Patzner R.A., Pointier J.P., Jackiewicz M., Meier-Brook C. & Mas-Coma S. (2001). "European Lymnaeidae (Mollusca: Gastropoda), intermediate hosts of trematodiases, based on nuclear ribosomal DNA ITS–2 sequences". Infection, Genetics and Evolution 1: 85–107.
- Bargues M. D., Artigas P., Jackiewicz M., Pointier J. P. & Mas-Coma S. (2005). "Ribosomal DNA ITS–1 sequence analysis of European Stagnicoline Lymnaeidae (Gastropoda)". Heldia 6(1/2): 57–68.
- (in Czech) Horsák M., Juřičková L., Beran L., Čejka T. & Dvořák L. (2010). "Komentovaný seznam měkkýšů zjištěných ve volné přírodě České a Slovenské republiky. [Annotated list of mollusc species recorded outdoors in the Czech and Slovak Republics]". Malacologica Bohemoslovaca, Suppl. 1: 1–37. PDF.
- Prie V. & Seddon M. B. (2011). "Stagnicola turricula". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2014.2. <www.iucnredlist.org>. Downloaded on 03 September 2014.
- "Species summary for Stagnicola turricula". AnimalBase, last modified 24 October 2008, accessed 3 September 2014.
- "Species summary for Stagnicola palustris". AnimalBase, last modified 24 February 2009, accessed 24 February 2011.
- (in Czech) Beran L. (2002). Vodní měkkýši České Republiky – rozšíření a jeho změny, stanoviště, šíření, ohrožení a ochrana, červený seznam. Aquatic molluscs of the Czech Republic – distribution and its changes, habitats, dispersal, threat and protection, Red List. Sborník přírodovědného klubu v Uherském Hradišti, Supplementum 10, 258 pp.
- (in German) Glöer P. & Meier-Brook C. (2003). Süsswassermollusken. DJN, pp. 134, page 109, ISBN 3-923376-02-2.
- Cordeiro J. & Perez K. (2012). "Stagnicola elodes". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2014.2. <www.iucnredlist.org>. Downloaded on 03 September 2014.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
