Thienothiophene
Thienothiophene usually refers to any of three structurally related derivatives of thiophene with the formula C6H4S2. In order of importance, they are: thieno(3,2-b)thiophene, thieno(2,3-b)thiophene, and thieno(3,4-b)thiophene. Other isomers feature S(IV) and are less stable.[1] Thieno[2,3-b]thiophene was the first member of the series to be isolated. It was obtained in very low yield upon heating citric acid, a source of a six-carbon linear chain, with P4S10.[2] More efficient syntheses of this and the other two stable thienothiophenes involve cyclization reactions of substituted thiophenes.[3]
Three thienothiophenes, being aromatic and bicyclic, are often compared with naphthalene. They are the topic of academic research. They have no commercial applications nor are they or their derivatives found naturally.
- Isomers of Thienothiophene
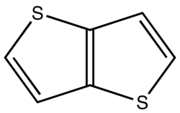
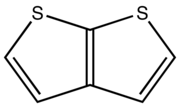 Thieno[2,3-b]thiophene
Thieno[2,3-b]thiophene
CAS RN 250-84-0
b.p. 102 °C at 16 mmHg
colorless oil.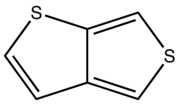 Thieno[3,4-b]thiophene
Thieno[3,4-b]thiophene
CAS RN 250-65-7
m.p. 7.0-7.5 °C
colorless oil..png.webp)
References
- Cava, Michael P.; Lakshmikantham, M. V. (1975). "Nonclassical Condensed Thiophenes". Accounts of Chemical Research. 8: 139–44. doi:10.1021/ar50088a005.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- V. P. Litvinov, Y. A. L. Gol'dfarb (1976). "The Chemistry of Thienothiophenes and Related Systems". Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry. 19. pp. 123–214. doi:10.1016/S0065-2725(08)60231-7.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Cinar, M. E.; Ozturk, T. (2015). "Thienothiophenes, Dithienothiophenes, and Thienoacenes: Syntheses, Oligomers, Polymers, and Properties". Chemical Reviews. 115: 3036–3140. doi:10.1021/cr500271a.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Nakayama, Juzo; Ishii, Akihiko; Kobayashi, Yasunobu; Hoshino, Masamatsu (1988). "Generation and Characterization of the Parent 2λ4δ2-Thieno[3,4-c]thiophene". Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications. 14: 959–60. doi:10.1039/C39880000959.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)