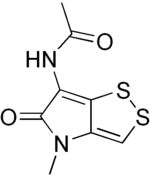
Thiolutin
Thiolutin is a sulfur-containing antibiotic, which is a potent inhibitor of bacterial and yeast RNA polymerases.[1] It was found to inhibit in vitro RNA synthesis directed by all three yeast RNA polymerases (I, II, and III). Thiolutin is also an inhibitor of mannan and glucan formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and used for the analysis of mRNA stability. Studies have shown that thiolutin inhibits adhesion of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) to vitronectin and thus suppresses tumor cell-induced angiogenesis in vivo.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | N-(8-methyl-7-oxo-3,4-dithia-8-azabicyclo[3.3.0]octa-1,5-dien-6-yl)acetamide, farcinicin, propiopyvothine, acetopyrrothine |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.163.691 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H8N2O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 228.28 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Thiolutin is formed in submerged fermentation by several strains of Streptomycetes luteosporeus. Some sources erroneously specify "aureothricin" as a synonym of thiolutin. Aureothricin is an antibiotic very similar to thiolutin, and is created as a by-product during the thiolutin fermentation.[2]
References
- Kebaara BW, Nielsen LE, Nickerson KW, Atkin AL (Aug 2006). "Determination of mRNA half-lives in Candida albicans using thiolutin as a transcription inhibitor". Genome. 49 (8): 894–9. doi:10.1139/g06-046. PMID 17036064.
- Fermentek product page