Thiophosphoric acid
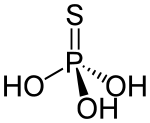
Thiophosphoric acid is a chemical compound. Structurally, it is the acid derived from phosphoric acid with one extra sulfur atom, although it cannot be prepared from phosphoric acid. It is a colorless compound that is rarely isolated in pure form, but rather as a solution. The structure of the compound has not been reported, but two tautomers are reasonable: SP(OH)3 and OP(OH)2SH.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H3PO3S | |
| Molar mass | 114.061 |
| Appearance | colorless |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Preparation
The compound has been prepared in a multistep process starting with the base hydrolysis of phosphorus pentasulfide to give dithiophosphate, which is isolated as its barium salt:[1]
- P2S5 + 6 NaOH → 2 Na3PO2S2 + H2S + 2 H2O
- 2 Na3PO2S2 + 3 BaCl2 → 2 Ba3(PO2S2)2 + 6 NaCl
In a second stage, the barium salt is decomposed with sulfuric acid, precipitating barium sulfate and liberating free dithiophosphoric acid:
- Ba3(PO2S2)2 + 3 H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2 H3PO2S2
Under controlled conditions, dithiophosphoric acid hydrolyses to give the monothioderivative:
H3PO2S2 + H2O → H3PO3S + H2S
References
- R. Klement "Phosphorus" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. Vol. 1. p. 570, 568.