Trans-Fly savanna and grasslands
The Trans Fly savanna and grasslands are a lowland ecoregion on the south coast of the island of New Guinea in both the Indonesian and Papua New Guinean sides of the island. With their monsoon and dry season climate these grasslands are quite different from the tropical rainforest that covers most of the island and resemble the landscape of northern Australia which lies to the south.
| Trans-Fly savanna and grasslands | |
|---|---|
 The Trans-Fly savanna in Papua New Guinea | |
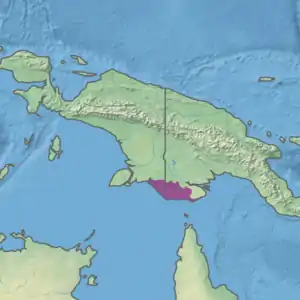 Ecoregion territory (in purple) | |
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Australasian |
| Biome | tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands |
| Borders | New Guinea mangroves, Southern New Guinea freshwater swamp forests, and Southern New Guinea lowland rain forests |
| Geography | |
| Area | 26,539 km2 (10,247 sq mi) |
| Countries | Indonesia and Papua New Guinea |
| Conservation | |
| Conservation status | Relatively stable/intact |
| Protected | 10419 km² (39%)[1] |
The name refers to the Fly River.
Flora
The area is mostly grassland that resembles nearby northern Australia and contains areas of eucalyptus, albizzia, and melaleuca woodland. The grasslands are renewed by regular fires at the end of the dry season.
Fauna
While the grasslands are not as rich in wildlife as the rainforests of New Guinea, they are home to a number of endemic species. Mammals of the area include the New Guinean planigale (Planigale novaeguineae), bronze quoll (Dasyurus spartacus), spectacled hare-wallaby (Lagorchestes conspicillatus) and dusky pademelon (Thylogale brunii). Birds of the area include the Fly River grassbird (Megalurus albolimbatus) and the spangled kookaburra, a famous relative of the kingfisher which feeds on rodents and reptiles rather than fish. The area has an important number of reptiles and amphibians including the unique pig-nosed turtle (Carettochelys insculpta).
Threats and preservation

This is a remote area with a large but very localised tribal population. Most habitats are intact although wildlife is vulnerable to collection, hunting and damage by logging and woodland clearance, especially as people migrate into the area on the Indonesian side. The grasslands are also modified by grazing of the introduced Javan rusa deer (Cervus timorensis). A third of the region is protected, particularly in Indonesia's large Wasur National Park on the coast and the adjoining Tonda Wildlife Management Area across the border in Papua New Guinea.[2]
References
- Eric Dinerstein, David Olson, et al. (2017). An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm, BioScience, Volume 67, Issue 6, June 2017, Pages 534–545; Supplemental material 2 table S1b.
- "Trans Fly savanna and grasslands". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.