Tropical Storm Beryl (1982)
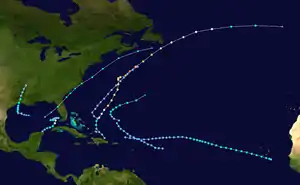
Tropical Storm Beryl was a deadly tropical storm which killed 3 people when it passed just south of the Cape Verde Islands. Beryl, the second named storm of the 1982 Atlantic hurricane season, developed out of a well organized tropical wave which was first noted near Dakar, Senegal on August 27. The wave was declared a tropical depression the next morning and upgraded it to a tropical storm later that same day. Beryl passed 35 mi (55 km) south of the island of Brava, Cape Verde by August 29. Beryl gradually intensified as it moved away from the islands and peaked just short of hurricane status on September 1 with peak winds of 72 mph (115 km/h). After peaking, Beryl quickly weakened to a tropical depression by the night of September 2. The depression continued on a general path towards the west until is dissipated on September 6 while located to the north of the Leeward Islands.
| Tropical storm (SSHWS/NWS) | |
 Tropical Storm Beryl in the eastern Atlantic Ocean | |
| Formed | August 28, 1982 |
|---|---|
| Dissipated | September 6, 1982 |
| Highest winds | 1-minute sustained: 75 mph (115 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 989 mbar (hPa); 29.21 inHg |
| Fatalities | 3 direct |
| Damage | $3 million (1982 USD) |
| Areas affected | Cape Verde Islands |
| Part of the 1982 Atlantic hurricane season | |
Meteorological history
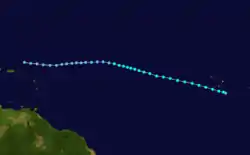
Tropical Storm Beryl originated from a well developed tropical wave which was first noted off the eastern coast of Africa on August 27. The wave quickly organized and strengthened into Tropical Depression Two on the morning of August 28. The depression continued to intensify while moving towards the west-northwest, and was upgraded to a tropical storm that night, receiving the name Beryl. Tropical Storm Beryl that night while moving towards the west-northwest. On the morning of August 29, Beryl passed about 35 mi (55 km) south of the island of Brava, Cape Verde with winds of 45 mph (75 km/h). After passing by the Cape Verde Islands, Beryl gradually intensified while moving steadily towards the northwest. On August 31, satellites depicted an eye feature developing within the deep convection of the storm. However, there was uncertainty in the intensity of the storm as the Dvorak technique—a system used to estimate the intensity of a tropical cyclone—rendered a T4.2, which corresponds to an intensity of 80 mph (130 km/h). But, since the eye feature was located on the western side of the deep convection and the storm was slightly asymmetric, the intensity was held just below hurricane status.[1] Beryl peaked just below hurricane status with winds reaching 70 mph (110 km/h).[2] Only four hours later, strong wind shear from the west displaced the convection east of the center, leaving the low-level circulation exposed.[1] Beryl weakened to a tropical depression the next day due to the lack of convection. The depression continued moving towards the west for the next three days without reintensification. However, on September 5, a reconnaissance flight into the depression found winds of 65 mph (100 km/h). This was determined to have been unrepresentative of the storms actual intensity as it was recorded in a squall line, a band of heavy rain and high winds, associated with Beryl. The depression became disorganized once more and by September 6, it was no longer identifiable on satellites.[3]
Impact, naming, and statistics
While crossing through the Cape Verde islands, Beryl's rain and wind to caused moderate to heavy damage. The island of Brava, located on the southwest portion of the archipelago, was struck the hardest. In all, the storm killed 3 islanders and caused $3 million in damage (1982 USD).[4][5] In the period after the storm's passage, the United States provided humanitarian aid and economic assistance to the country, helping the archipelago to reverse the effects of Beryl.[6] Despite the death toll, the name Beryl was not retired and was re-used in 1988, 1994, 2000 and most recently in 2006 and is currently on the list of names for the 2012 Atlantic hurricane season.[7]
See also
- Other storms named Beryl
- List of West Africa hurricanes
- Tropical Storm Christine (1973) – Easternmost-forming tropical or subtropical storm on record, until the formation of Subtropical Storm Alpha (2020)
- Hurricane Fred (2015) – Struck Cape Verde, causing significant damage
References
- National Hurricane Center (1983). "Tropical Storm Beryl Preliminary Report, Page One". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
- Dan Vietor (2005). "Tropical Storm Beryl 1982 trackfile (Unisys)". Unisys Corporation. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
- National Hurricane Center (1983). "Tropical Storm Beryl Preliminary Report, Page Two". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
- http://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/PNABP986.pdf
- EM-DAT: the International Disaster Database (2007). "Disaster List for Cape Verde". Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters. Retrieved 2007-03-08.
- Geography I.Q. (2007). "U.S.-CAPE VERDEAN RELATIONS". Geography I.Q. Retrieved 2007-04-05.
- NHC (2008). "Atlantic Best Tracks, 1851 to 2007". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2008-11-01.