Typographer (typewriter)
The typographer was an early typewriter. It was a mechanical innovation created by William Austin Burt. The mechanism was operated by hand to provide a printed ink impression on paper. Burt was a government surveyor and needed to get official correspondence done quickly. He observed office workers overwhelmed with laborious tasks of handwriting lengthy official documents that took a long time. Burt had a mechanical background so was inspired to make a machine that would speed up secretarial work. A friend of his in the newspaper business furnished typeface letters from a printing press for his experimental mechanism.
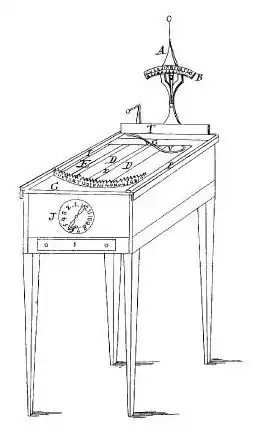
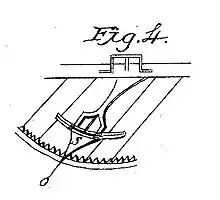
Burt had two versions of his mechanical apparatus. The first was built in a wooden box that could be carried by hand. The second was a large advanced model that was mounted on four legs. The first working model provided by Burt for his 1829 patent was destroyed in the 1836 Patent Office fire. Although his typographer, as his innovation was first known by, could print neat documents the mechanism was slow as each letter had to be done by hand. His invention ultimately did not accomplish the goal of speeding up office work as he had intended.
History
Burt conceived the idea of a typing device when he observed office workers overwhelmed with the task of creating official documents in triplicate by hand. He reasoned that a printing machine could relieve many hours of the tedious task by automation. In the 1820s in his blacksmith shop he commenced the development of such an apparatus. His "typographer" constructed to the point of being able to print out a neat letter was patented as number 259 on July 23, 1829.[2][3][4]
United States Patent Office documents describe Burt's American machine as "the actual construction of a type writing machine for the first time in any country".[5] It was the first practical typewriting machine ever made in America,[6] although Pellegrino Turri had made one in Italy in 1808.[7] The patent gave Burt the full exclusive rights to his new typewriter machine for 14 years, including vending or selling to others any or all of these rights as he saw fit, signed by President Andrew Jackson.[8]
All "type writing" machines, those that used letters of typeface, were generally given the name "typographer" from Burt's 1829 patent until 1874 by subsequent inventors who improved on Burt's machine.[9] The concept ultimately came to be called a "type-writer" in 1874.[10][11] The word stayed hyphenated until the 1880s. William Ozmun Wyckoff, president of the New York State Shorthand Reporters' Association in 1886, and founder of the Remington Typewriter Company, publicized the unhyphenated name "typewriter". It became very well known, and the public finally accepted this as one word by 1919.[12] Eventually, Burt's typographer was called a typewriter.[13]
In 1714, the British patent office issued a patent to English engineer Henry Mill for a typewriter; however, he never built it.[14] This first record of an initial attempt gave Mills time (14 years) to develop a model or at least a description of his "artificial machine"; however, the secret of how to make such a machine, if there ever was one, died with him.[15] There is no record that it ever existed.[16] There hasn't even been found a trace of any drawings or specifications.[17]
Christopher Latham Sholes is given credit for inventing the first "practical" typewriter.[18] He was in fact the fifty-second person or possibly the 112th to reinvent a "type-writing" machine – which he called a type-writer.[19][20] Some of the "type-writing" machines invented between Burt's 1829 patented machine and Sholes' 1867 type-writer are "The Projean Machine" (1833), "The Thurber Machine" (1843), "The Foucault Machine" (1843), "O. T. Eddy's machine" (1850), "The Fairbanks machine" (1850), "J. M. Jones' machine" (1850), "William Hughes' machine" (1851), John M. Jones "mechanical Typographer" (1852), "Thomas' typograph" (1854), "The Beach typewriter" (1856), "The Francis Typewriter" (1857), "The Hansen Machine" (1865), "The Livermore Printing Device" (1863), "Peeler Writing Machine" (1866), and "The Sholes and Glidden Typewriter" (1867) invented by three men (C. Latham Sholes, Samuel W. Soule, Carlos Glidden).[18][21] Thomas Edison is even given credit for an electrified version in 1872.[18]
The Board of Electors at the National Shorthand Association of Detroit recognized Burt as a leader among typewriter inventors and one that ensured world-wide recognition of priority of American inventors in the typewriter field. French authors Henri Dupont and C. Senechal described Burt's typographer in great detail in their 1906 book Les machines a écrire: historique, avantages, descriptions et traité complet de dactylographie ou art d'écrire a la machine.[22]
Patent

The machine was a rectangular wooden box 12 in (300 mm) wide, 12 in (300 mm) high, and 18 in (460 mm) long. It mechanically worked by depressing a rotating lever so that an inked letter made contact with paper. A gauge that was designed in a circular clockwise fashion on the front of the box indicated the number of lines typed on the blank piece of paper that was up to 15 inches in length. The paper was attached to a velvet-like material belt. The belt rotated when the impression lever was depressed.[23]
The patent describes Burt's machine as having a set of typeface characters that were arranged on the under side of a set of parts that had a lever pivoted to swing vertically and horizontally. The desired typeface character is brought to the printing point by moving this lever horizontally to a position over the same character in the index, and the impression on the paper is made by then depressing the lever. Different styles of typeface characters could be used. They were arranged in two rows on a lever. The rows of typeface characters could be shifted on the lever to bring either one to the printing point. The paper was carried in an endless band that traveled crosswise of the machine and the band was moved for letter space by the impression lever every time the lever is depressed to print. The line space was made by shifting the frame carrying the printing mechanism toward the front or rear of the machine, with the paper remaining stationary. Ink-pads were located at each side of the impression point, and all the typeface characters, except the one in the printing position, were inked every time the impression lever was depressed. Upper and lower case typeface letters could be used. A dial was provided that indicated the length of paper (inches) which had passed the printing point in printing each line. The operator knew the width of the paper being used each time. There was a stop printing indicator for end of the line.[6]
Four classes of typewriters had been recognized by the U. S. Patent Office. The first was an index-wheel machine, like that patented by Burt on July 23, 1829. The second was the bar-machine first patented by John B. Fairbanks on September 17, 1850. The third was the plate-machine first patented by Oliver T. Eddy on November 12, 1850. The fourth was the key-wheel machine first patented by John Pratt on August 11, 1868.[24]
A complete working model of Burt's "typographer" was in the model room of the Patent Office from the time of the patent until the Patent Office fire of December 15, 1836.[6][9][25] The fire destroyed all the patents and patent models issued from 1790.[26] A competent mechanic can build a working replica of Burt's typographer from his patent description and drawings.[24] Austin Burt, the great grandson of Burt, built a working model in 1892 for the World's Columbian Exposition working from a parchment copy of the original patent (No. 5581X).[6][27][28]
The reason Burt built the machine was to speed up his work in official correspondence as a government surveyor. John Pitts Sheldon of the Detroit Free Press, Burt's newspaper editor friend, furnished the typeface letters from the newspaper company in May 1829 for Burt's first typographer to be able to type the first letter ever written on it. The letter was to future president Martin Van Buren then Secretary of State. Two months later it received an official patent as one of the most unique and useful inventions of the time. It was the first patent for a type writing machine.[29]
Burt built in 1830 a second improved typographer typewriter that resembled a pinball machine because four tapered legs for standing were added to it.[29] Sheldon had taken Burt's "moddle" to the Patent Office in Washington, D.C. on March 9 of that year according to a typewritten letter to his wife of March 13, 1830.[30] The typeface letters for this Patent Office model was obtained from a Mr. White of New York, a typeface founder.[27] Even though a neat-looking letter could be typed on Burt's "typographer", the basic goal to speed up correspondence was not accomplished, as his machine was very slow in typing. Because of this, the machine could not get marketed. Burt lost interest in it and sold his rights to one Cyrus Spalding for $75 on March 17, 1830 with suggested improvements. Ultimately he did not have any further luck in marketing the typewriter.[31] The typographer was so far ahead of its time it found no market.[6]
 Typed typographer letter by Burt in 1830 to his wife[30]
Typed typographer letter by Burt in 1830 to his wife[30] Letters Patent 1829 – signed by President Andrew Jackson
Letters Patent 1829 – signed by President Andrew Jackson
References
- "The 'Inventor' of the Typewriter". The Times-Independent. Moab, Utah. February 6, 1936. p. 6 – via Newspapers.com
 .
. - Meyers 1995, p. 48.
- "First Letter Ever Written on a Typewriter Finds its Way Here". The Gazette. Cedar Rapids, Iowa. July 10, 1922. p. 5 – via Newspapers.com
 .
. - Cox, John A. (August 9, 1953). "Patron Saint of Stenographers". Hartford Courant. Hartford, Connecticut. p. 112 – via Newspapers.com
 .
. - Fuller 1922, p. 191.
- White 1922, pp. 367–368.
- Revett, Kenneth (September 15, 2008). Behavioral Biometrics: A Remote Access Approach. John Wiley & Sons. p. 222. ISBN 9780470997932. Retrieved June 28, 2014.
- Burt 1986, p. 14.
- Kidder 1921, p. 12.
- White 1922, pp. 367-368.
- Baron, p. 201
- Fuller 1922, p. 189.
- Kane 2006, p. 299 #3585.
- Kane, item 3585
- Melville, Arthur (October 1923). "The Machine Gun of Commerce". The Rotarian, Vol.23, No.4. New York City: Rotary International. ISSN 0035-838X. Retrieved July 11, 2020.
- Appleton 1900, p. 7.
- Burt 1986, p. 22.
- Linnoff 2000, pp. 10–14.
- Baron, p. 200
- Adler 1973, p. 159.
- Appleton 1900, p. 8.
- Fuller 1922, p. 193.
- Burt 1986, p. 13.
- Fuller 1922, p. 188.
- "How the 'blind writer' finally found its way into your office". National Post. Toronto, Canada. September 10, 1966. p. 52 – via Newspapers.com
 .
. - "The Inventor of the Typewriter May Find a Niche in the Hall of Fame". The Kansas City Times. Kansas City, Missouri. September 11, 1931. p. 18 – via Newspapers.com
 .
. - Burt 1986, p. 21.
- "Replica of First Typewriter in Hands of Austin Burt, Descendant of Maker". The Courier. Waterloo, Iowa. June 17, 1922. p. 5 – via Newspapers.com
 .
. - Gary Peters (October 24, 1979). "World's First Writing Machine". The Sheboygan Press. Sheboygan, Wisconsin. p. 47 – via Newspapers.com
 .
. - Fuller 1922, p. 192.
- Michigan History Magazine, article: "Willian Austin Burt", January 1922
Sources
- Adler, Michael H. (1973). The Writing Machine, A History of the Typewriter. George Allen & Unwin Ltd. ISBN 0-04-652004-X.
- Appleton, D. (1900). Universal Cyclopaedia, Vol. 12. D. Appleton. OCLC 861656957.
- Burt, James A. (1986). William Austin Burt and sons, surveyors of public domain. Landmark Enterprises. ISBN 0-910845-31-X.
- Fuller, George Newman (1922). Michigan history, Volume 6. Michigan Department of State. OCLC 983255566.
- Kane, Joseph Nathan (2006). Famous first facts of inventions in American history. H.W. Wilson. ISBN 0-8242-1065-4.
- Kidder, Harry M. (1921). Transactions of the New York State Shorthand Reporters' Association at the fourth–fifth annual meeting held at December 28, 1920. Boyd Printing Company.
- Linnoff, Victor M. (2000). The Typewriter, an illustrated history. Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-41237-7.
- Meyers, Melanie (1995). An Octagon for the Curriers. Post Publications. ISBN 978-09645-9160-8.
- White, James T. (1922). Cyclopedia of American Biography, Volume 18. J. T. White. OCLC 164589128.