Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region of Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau.[1] It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after the UK's Queen Victoria.[1] The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south.
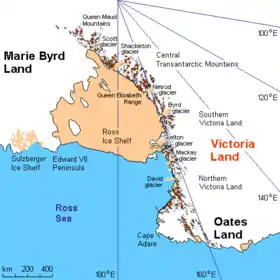
The region includes ranges of the Transantarctic Mountains and the McMurdo Dry Valleys (the highest point being Mount Abbott in the Northern Foothills), and the flatlands known as the Labyrinth. Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson.[2]
List of mountains of Victoria Land
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Victoria Land. |
- "Victoria Land". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2007-01-04.
- "Victoria Land". The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition. Columbia University Press. 2001. Archived from the original on 2006-02-11. Retrieved 2008-01-26.