Vinyl polymer
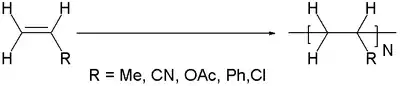
Vinyl polymers are a group of polymers derived from vinyl monomers of the type CH2=CHR. Their backbone is an extended alkane chain ...-CH2-CHR-CH2-CHR-..).[1] In popular usage, "vinyl" refers only to polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Examples
Vinyl polymers are the most common type of plastic. Important examples can be distinguished by the R group in the monomer H2C=CHR:
- Polyethylene R = H
- polypropylene from propylene, R = CH3
- Polystyrene is made from styrene, R = C6H5
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is made from vinyl chloride, R= Cl
- Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) is made from vinyl acetate, R = O2CCH3
- Polyacrylonitrile is made from acrylonitrile, R = CN
Vinyl polymers are produced using catalysts. Ziegler–Natta catalyst is a typical commercial catalyst for polyethylene and polypropylene.
See also
References
- Kenneth S. Whiteley,T. Geoffrey Heggs, Hartmut Koch, Ralph L. Mawer, Wolfgang Immel (2005). "Polyolefins". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a21_487.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.