Virtual displacement
In analytical mechanics, a branch of applied mathematics and physics, a virtual displacement (or infinitesimal variation) shows how the mechanical system's trajectory can hypothetically (hence the term virtual) deviate very slightly from the actual trajectory of the system without violating the system's constraints.[1][2][3]:263 For every time instant is a vector tangential to the configuration space at the point The vectors show the directions in which can "go" without breaking the constraints.
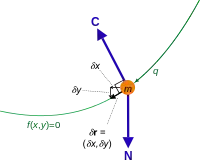
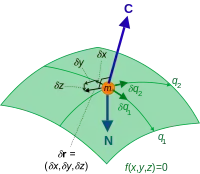
For example, the virtual displacements of the system consisting of a single particle on a two-dimensional surface fill up the entire tangent plane, assuming there are no additional constraints.
If, however, the constraints require that all the trajectories pass through the given point at the given time i.e. then
Notations
Let be the configuration space of the mechanical system, be time instants, and
The constraints are here for illustration only. In practice, for each individual system, an individual set of constraints is required.
Definition
For each path and a variation of is a function such that, for every and The virtual displacement being the tangent bundle of corresponding to the variation assigns[1] to every the tangent vector
In terms of the tangent map,
Here is the tangent map of where and
Properties
- Coordinate representation. If are the coordinates in an arbitrary chart on and then
- If, for some time instant and every then, for every
- If then
Examples
Free particle in R3
A single particle freely moving in has 3 degrees of freedom. The configuration space is and For every path and a variation of there exists a unique such that as By the definition,
which leads to
Free particles on a surface
particles moving freely on a two-dimensional surface have degree of freedom. The configuration space here is
where is the radius vector of the particle. It follows that
and every path may be described using the radius vectors of each individual particle, i.e.
This implies that, for every
where Some authors express this as
Rigid body rotating around fixed point
A rigid body rotating around a fixed point with no additional constraints has 3 degrees of freedom. The configuration space here is the special orthogonal group of dimension 3 (otherwise known as 3D rotation group), and We use the standard notation to refer to the three-dimensional linear space of all skew-symmetric three-dimensional matrices. The exponential map guarantees the existence of such that, for every path its variation and there is a unique path such that and, for every By the definition,
Since, for some function , as ,
See also
References
- Takhtajan, Leon A. (2017). "Part 1. Classical Mechanics". Classical Field Theory (PDF). Department of Mathematics, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY.
- Goldstein, H.; Poole, C. P.; Safko, J. L. (2001). Classical Mechanics (3rd ed.). Addison-Wesley. p. 16. ISBN 978-0-201-65702-9.
- Torby, Bruce (1984). "Energy Methods". Advanced Dynamics for Engineers. HRW Series in Mechanical Engineering. United States of America: CBS College Publishing. ISBN 0-03-063366-4.