Vitamin D deficiency in Australia
Vitamin D deficiency has become a worldwide health epidemic with clinical rates on the rise. In the years of 2011–12, it was estimated that around 4 million adults were considered deficient in Vitamin D throughout Australia.[1] The Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) found 23%, or one in four Australian adults suffer from some form of Vitamin D deficiency.[1] Outlined throughout the article are the causes of increase through subgroups populations, influencing factors and strategies in place to control deficiency rates throughout Australia.
Background
Importance of vitamin D
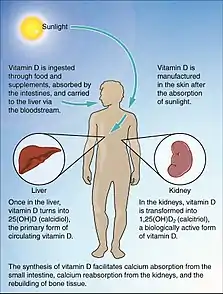
Vitamin D plays an important role in which it supports calcium absorption in the body, sustaining good bone health as well as muscle function. When calcium in the body becomes under provided for normal bodily functions, calcitriol, an active form of Vitamin D, pairs with parathyroid hormone. Together they act to assemble cells in order to increase the calcium stores taken from bone.[2]
The popular term Sunshine vitamin, as it's often called, is one of the one main sources of achieving sufficient Vitamin D through sunlight on the skin known as D3. The second form is commonly known as D2, which is found in foods such as fatty fish and fortified products like margarine and milk.[1]
Additionally, if you consume vitamin D through your diet, or make vitamin D in your skin from UVB exposure, it is processed through two organs before it becomes activated. Vitamin D is first processed in the liver, before heading to the kidneys where it becomes activated to the form 1-25 dihydroxy vitamin D or alternatively named chemical calcitriol.[3]
Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency historically used to be identified through counting cases of rickets. The old theory was that if someone had enough vitamin D to prevent rickets and osteomalacia, two skeletal disorders, they were considered safe from a deficiency. Nowadays through technological advancements Vitamin D deficiencies are now identified and thus calculated through the measurement of the serum 25-OH. According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics National Health Measures Survey (NHMS), the recommend Vitamin D levels to determine deficiency are categorised as follows:
•Adequate levels: > 50 nmol/L
•Mild deficiency: 30-49 nmol/L
•Moderate deficiency: 13 – 29nmol/L
•Severe deficiency: < 13 nmol/L [4]
In 1997, the prevalence of deficiency, defined as <17.5 nmol/L, was 2.8%, and the prevalence of insufficiency, defined as <37.5 nmol/L, was 27.6% among Australians over the age of 15.[5] In 2011-2012 23% of Adults had a deficiency defined as below 49 nmol/L.[6]
Health effects
This fundamental fat-soluble vitamin has been long known for its important role in calcium absorption in the body, especially in musculoskeletal health. The health impacts commonly caused by deficiency of Vitamin D are rickets in children and osteoporosis in the elderly populations. Low levels of Vitamin D have also been associated with other conditions such as heart disease, cancer and kidney disease but further research is required.[1] Recent evidence suggests Vitamin D is also linked to many other health diseases such as cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis and some form of cancer.[7]
Rickets

Rickets can be traced back to the 1600s, where a pandemic arose with children around the globe from Vitamin D deficiency.[8] The inadequate intake of UV exposure consequently lead children to numerous health problems such as, growth retardation, muscle weakness, skeletal deformities, hypocalcemia, tetany and seizures.[8] During the late 19th century autopsies conducted in the Netherlands concluded that 80-90% of children were suffering from Rickets.[8] The incidents of rickets observed within Sydney hospitals during the years of 2003 – 2004 have doubled. This major spike can be attributed to the growing population of migrants in Australia, many of whom are considered high risk of vitamin D deficiency.[2]
As shown in the image the skeletal deformities such as knock knees and bow legs in these young children as a result of rickets.
Osteoporosis
Because of the high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency, conditions such as osteoporosis alongside Australia's aging population have now seen many Australians over 60 suffering this now wide spread condition among the elderly. Osteoporosis can be defined as very fragile and brittle bones, in which serious fractures can occur with just the slightest bump or fall.[9] Osteoporosis Australia have predicted that half of all women and one third of men all men over the age of 60 years will suffer the debilitating effects of osteoporosis.[9]
Osteoporosis also commonly known as the silent disease as in most cases individuals don't know they are affected until they fracture a bone as a result from a fall.[9]
High risk groups
Age
Several studies conducted in Australia have revealed deficiency ranging from 15-52% amongst the senior populations. These deficiencies have been found to be higher amongst those who are homebound or living within institutions with less access sun exposure.[10] Vitamin D concentration levels below 28 nmol/L are common amongst the studies conducted. Throughout Sydney nursing home studies, it has revealed that 86% of woman and 68% of men are falling into moderate deficiency ranges.[2]
In a study based in Western Australia, 63% of patients admitted with hip fractures were observed to have serum levels less than 50 nmol/L in comparison to the 25% to the controlled.[2]
Skin colour
In Australia, vitamin D deficiency has been recognised within particular subgroups such as age, dark skinned and veiled women.[11] There is deficiencies in around 80%, particularly in dark skinned and or veiled populations.[12] The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency amongst dark skinner or who cover their skin for religious reasons can be directly attributed to the extremely low of sun exposure to which is the main source of vitamin D in Australia.
Veiled women or individuals with dark skin pigmentation are easily vulnerable to fall into levels considered deficient in Australia. This is most likely because of the clothing worn acts as a direct barrier as well as absorbing the UVB irradiation.[13] Dark Skin also has high levels of melanin pigmentation which decreases the cutaneous production of vitamin D. African-Americans require six times more UVB dosages to stimulate the production of vitamin D in the skin, compared with those of European descendants.[13]
Sun exposure
Despite Australia having a sunlit climate, Australians are remarkably falling short of adequate levels ultraviolet B (UVB) light from the sun. Associated factors contributing to the low vitamin D levels are seasonal variations such as winter, where there is minimal sun exposure, less time spent outdoors and people covering up due to the cold weather.[2] Environmental influences that impact the vitamin D production are the angle of the sun, distance from the equator, latitudes and amount of cloud cover.
To ensure adequate vitamin D levels are reached, an average daily amount, roughly 10% of the sunburn threshold is required on a sensible amount of skin, not just the backs of hands. A burn time for a fair-skinned person could be limited to just 8 minutes in the middle of the day, during summer without sunscreens. A dark skinned or covered individual might need hours to achieve that same desired amount. The strength of the UVB changes throughout the day so time will be change accordingly.[3]
Obesity
There is conflicting evidence to suggest whether obesity contributes to vitamin D deficiency. Obese individuals have an increased risk of being vitamin D deficient likely caused by lack of sun exposure from reduced mobility and or low levels of physical activity.[11] The serum levels of obese Australian were 8.3- 9.5 nmol/L lower in both genders comparable to those of healthy weight ranges.[11] During the AusDiab study conducted throughout Australia serum levels within obese people were shown to be 57% lower than with normal weight after receiving the same amount of UV exposure.[11]
Inconsistent to the findings of AusDiab Study, The Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) found there to be no correlation between weight levels and vitamin D serum level.[4] According to ABS the Vitamin D supplementation was said to not be a contributing factor as supplement use was similar across all weight ranges.[4]
Pregnancy
Pregnancy also poses as another high risk factor for vitamin D deficiency. The status levels of vitamin D during the last stages of pregnancy directly impact the newborns first initial months of life.[10] Babies who are exclusively breastfed with minimal exposure to sunlight or supplementation can be at greater risk of vitamin D deficiency, as human milk often has minimal vitamin D present. Recommendations for infants of the age 0–12 months are set at 5 ug/day, to assist in preventing rickets in young babies.[10] 80% of dark skinned and or veiled women in Melbourne were found to have serum levels lower than 22.5 nmol/L considering them to be within moderate ranges of vitamin D deficiency.[2]
Contributing factors
Australia's vitamin D deficiency levels in recent years have been on the increase, due to factors such as the long-term success of SunSmart government campaigns like Slip, Slop, Slap as well as Cancer Council Australia that have increased the general public's awareness of the risks associated with excessive sun exposure and skin cancers.[3] The 'sun smart' campaign created in 1988 had a significant impact on the public approach and behaviours towards sun exposure.[14] The success of this campaign reduced the sunburn rate by 50%, which researchers believe to have contributed to the rise in vitamin D deficiencies across Australia.[14]
In addition to the reduced sun exposure amongst the Australia populations, there have been decreases in the form of dietary intake as many people are no longer taking fatty fish oil tablets as a method of regulating vitamin D.[3]
Other factors previously mentioned are sun exposure, geographical longitude as well as season change. Greater latitudes receive sunlight that is of lesser ultra radiation strength in contrast to regions close to the equator, who receive lower variation to hours of daylight during the summer periods.[7]
Government strategies
Mandatory fortification

In light of the increase of vitamin D deficiency throughout Australia the federal government introduced mandatory fortification of vitamins and minerals such as vitamin D in certain foods like edible oil spreads as indicated in the: Australian Standard 2.4.2.[15] It is mandatory for all food manufacturing companies producing table spreads like butter and margarine to have no less than 55 mg/kg of vitamin D, as a response to a growing public health requirements.[15]
In response to recent advances, public policies are being reconsidered to ensure vitamin D is evidently being measured.[2] With the vitamin D deficiency resurfacing the nutrient reference value guidelines were established, in turn creating the dietary vitamin D recommendations.[2]
The dietary vitamin D guidelines are assuming limited exposure to UVB sunlight are:
Infants, Children and Adults < 50 years: 5 μg/day (200 IU/day)
Adults > 50 - < 70 years: 10 μg/day (400 IU/day)
Adults > 70 years: 15 μg/day (600 IU/day)[2]
Treatment
Day to day requirements of vitamin D are set around 800-1000IU to maintain healthy levels which in most cases can be provided by sun exposure. Increased amounts are required for individuals who are previously diagnosed as deficient. For those of moderate deficiencies, oral supplementation can be implemented into the diet at levels of 3000-5000 IU per day for a 6- to 12-week period continued by an ongoing reduced dose of 1000- 2000 IU per day to maintain stores in the body.
Severe deficiency is treated through megadose therapy where patients are given doses around 100 000 IU to assist in raising stores faster to ensure physical health in restored to prevent further illness or disease.[16]
See also
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Vitamin D
- Sun exposure
References
- "Australian Health Survey: Biomedical Results for Nutrients, 2011-12" (PDF).
- Shrapnel, William; Truswell, Stewart (2006-12-01). "Vitamin D deficiency in Australia and New Zealand: What are the dietary options?". Nutrition & Dietetics. 63 (4): 206–212. doi:10.1111/j.1747-0080.2006.00080.x. ISSN 1747-0080.
- "Vitamin D". Radio National. Retrieved 2015-09-02.
- "Australian Health Survey: Biomedical Results for Nutrients,2011-12" (PDF).
- https://www.nrv.gov.au/nutrients/vitamin-d
- https://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/Lookup/4364.0.55.006Chapter2002011-12
- Quaggiotto, P; Tran, H; Bhanugopan, M (2014-01-01). "Vitamin D deficiency remains prevalent despite increased laboratory testing in New South Wales, Australia". Singapore Medical Journal. 55 (5): 271–280. doi:10.11622/smedj.2014071. PMC 4291993. PMID 24862752.
- Holick, M. F. (2006-01-01). "Resurrection of vitamin D deficiency and rickets". Journal of Clinical Investigation. 116 (8): 2062–2072. doi:10.1172/jci29449. PMC 1523417. PMID 16886050.
- "Calcium, Vitamin D and Osteoporosis" (PDF).
- "Vitamin D | Nutrient Reference Values". www.nrv.gov.au. 2014-03-17. Retrieved 2015-09-02.
- Daly, Robin M.; Gagnon, Claudia; Lu, Zhong X.; Magliano, Dianna J.; Dunstan, David W.; Sikaris, Ken A.; Zimmet, Paul Z.; Ebeling, Peter R.; Shaw, Jonathan E. (2012-07-01). "Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its determinants in Australian adults aged 25 years and older: a national, population-based study". Clinical Endocrinology. 77 (1): 26–35. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04320.x. ISSN 1365-2265. PMID 22168576.
- "VItamin D in Australia" (PDF).
- "Vitamin D deficiency and multicultural Australia". The Medical Journal of Australia. 2001.
- Timms, Brad (2002). ""Slip, Slop, Slap" campaign may need rethink". Oncology. 3 (10): 588. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(02)00892-6.
- "Vitamins and minerals added to food". www.foodstandards.gov.au. Retrieved 2015-09-03.
- "Vitamin D deficiency in adults". 2010.