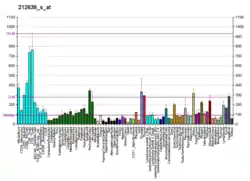
WWP1
NEDD4-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase WWP1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the WWP1 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
WW domain-containing proteins are found in all eukaryotes and play an important role in the regulation of a wide variety of cellular functions such as protein degradation, transcription, and RNA splicing. This gene encodes a protein which contains 4 tandem WW domains and a HECT (homologous to the E6-associated protein carboxyl terminus) domain. The encoded protein belongs to a family of NEDD4-like proteins, which are E3 ubiquitin-ligase molecules and regulate key trafficking decisions, including targeting of proteins to proteosomes or lysosomes. Alternative splicing of this gene generates at least 6 transcript variants; however, the full length nature of these transcripts has not been defined.[7] In neurons, murine ortholog Wwp1 and its homolog Wwp2 control polarity acquisition, formation, and branching of axons, as well as migration of newly born nerve cells into the cortical plate.[8]
References
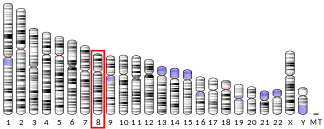
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000123124 - Ensembl, May 2017
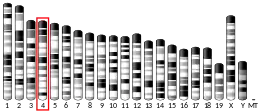
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000041058 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Pirozzi G, McConnell SJ, Uveges AJ, Carter JM, Sparks AB, Kay BK, Fowlkes DM (June 1997). "Identification of novel human WW domain-containing proteins by cloning of ligand targets". J Biol Chem. 272 (23): 14611–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.23.14611. PMID 9169421.
- Wood JD, Yuan J, Margolis RL, Colomer V, Duan K, Kushi J, Kaminsky Z, Kleiderlein JJ, Sharp AH, Ross CA (July 1998). "Atrophin-1, the DRPLA gene product, interacts with two families of WW domain-containing proteins". Mol Cell Neurosci. 11 (3): 149–60. doi:10.1006/mcne.1998.0677. PMID 9647693. S2CID 20003277.
- "Entrez Gene: WWP1 WW domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1".
- Ambrozkiewicz MC, Schwark M, Kishimoto-Suga M, Borisova E, Hori K, Salazar-Lázaro A, Rusanova A, Altas B, Piepkorn L, Bessa P, Schaub T, Zhang X, Rabe T, Ripamonti S, Rosário M, Akiyama H, Jahn O, Kobayashi T, Hoshino M, Tarabykin V, Kawabe H (December 2018). "Polarity Acquisition in Cortical Neurons Is Driven by Synergistic Action of Sox9-Regulated Wwp1 and Wwp2 E3 Ubiquitin Ligases and Intronic miR-140". Neuron. 100 (5): 1097–1115.e15. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2018.10.008. PMID 30392800.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (October 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Conkright MD, Wani MA, Lingrel JB (August 2001). "Lung Krüppel-like factor contains an autoinhibitory domain that regulates its transcriptional activation by binding WWP1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (31): 29299–306. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103670200. PMID 11375995.
- Qin H, Pu HX, Li M, Ahmed S, Song J (Dec 2008). "Identification and structural mechanism for a novel interaction between a ubiquitin ligase WWP1 and Nogo-A, a key inhibitor for central nervous system regeneration". Biochemistry. 47 (51): 13647–58. doi:10.1021/bi8017976. PMID 19035836.
Further reading
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Mosser EA, Kasanov JD, Forsberg EC, Kay BK, Ney PA, Bresnick EH (1998). "Physical and functional interactions between the transactivation domain of the hematopoietic transcription factor NF-E2 and WW domains". Biochemistry. 37 (39): 13686–95. doi:10.1021/bi981310l. PMID 9753456.
- Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, Gassenhuber J, Glassl S, Ansorge W, Böcher M, Blöcker H, Bauersachs S, Blum H, Lauber J, Düsterhöft A, Beyer A, Köhrer K, Strack N, Mewes HW, Ottenwälder B, Obermaier B, Tampe J, Heubner D, Wambutt R, Korn B, Klein M, Poustka A (2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs". Genome Res. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- Conkright MD, Wani MA, Lingrel JB (2001). "Lung Krüppel-like factor contains an autoinhibitory domain that regulates its transcriptional activation by binding WWP1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (31): 29299–306. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103670200. PMID 11375995.
- Flasza M, Gorman P, Roylance R, Canfield AE, Baron M (2002). "Alternative splicing determines the domain structure of WWP1, a Nedd4 family protein". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 290 (1): 431–7. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.6206. PMID 11779188.
- Galinier R, Gout E, Lortat-Jacob H, Wood J, Chroboczek J (2003). "Adenovirus protein involved in virus internalization recruits ubiquitin-protein ligases". Biochemistry. 41 (48): 14299–305. doi:10.1021/bi020125b. PMID 12450395.
- Verdecia MA, Joazeiro CA, Wells NJ, Ferrer JL, Bowman ME, Hunter T, Noel JP (2003). "Conformational flexibility underlies ubiquitin ligation mediated by the WWP1 HECT domain E3 ligase". Mol. Cell. 11 (1): 249–59. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00774-8. PMID 12535537.
- Komuro A, Imamura T, Saitoh M, Yoshida Y, Yamori T, Miyazono K, Miyazawa K (2004). "Negative regulation of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) signaling by WW domain-containing protein 1 (WWP1)". Oncogene. 23 (41): 6914–23. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207885. PMID 15221015. S2CID 7742985.
- Colland F, Jacq X, Trouplin V, Mougin C, Groizeleau C, Hamburger A, Meil A, Wojcik J, Legrain P, Gauthier JM (2004). "Functional proteomics mapping of a human signaling pathway". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1324–32. doi:10.1101/gr.2334104. PMC 442148. PMID 15231748.
- Seo SR, Lallemand F, Ferrand N, Pessah M, L'Hoste S, Camonis J, Atfi A (2005). "The novel E3 ubiquitin ligase Tiul1 associates with TGIF to target Smad2 for degradation". EMBO J. 23 (19): 3780–92. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600398. PMC 522797. PMID 15359284.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Chen C, Sun X, Guo P, Dong XY, Sethi P, Cheng X, Zhou J, Ling J, Simons JW, Lingrel JB, Dong JT (2006). "Human Kruppel-like factor 5 is a target of the E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP1 for proteolysis in epithelial cells". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (50): 41553–61. doi:10.1074/jbc.M506183200. PMID 16223724.
- Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C, Patel AJ, Szabó G, Rual JF, Fisk CJ, Li N, Smolyar A, Hill DE, Barabási AL, Vidal M, Zoghbi HY (2006). "A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration". Cell. 125 (4): 801–14. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.032. PMID 16713569. S2CID 13709685.
- Flasza M, Nguyen Huu NS, Mazaleyrat S, Clémence S, Villemant C, Clarke R, Baron M (2006). "Regulation of the nuclear localization of the human Nedd4-related WWP1 protein by Notch". Mol. Membr. Biol. 23 (3): 269–76. doi:10.1080/09687860600665010. PMID 16785210. S2CID 913524.
- Laine A, Ronai Z (2007). "Regulation of p53 localization and transcription by the HECT domain E3 ligase WWP1". Oncogene. 26 (10): 1477–83. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209924. PMC 2997392. PMID 16924229.
- Chen C, Sun X, Guo P, Dong XY, Sethi P, Zhou W, Zhou Z, Petros J, Frierson HF, Vessella RL, Atfi A, Dong JT (2007). "Ubiquitin E3 ligase WWP1 as an oncogenic factor in human prostate cancer". Oncogene. 26 (16): 2386–94. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210021. PMID 17016436. S2CID 24487179.