Xylylene dichloride
The chemical compound xylylene dichloride (C8H8Cl2) is a white to light yellow sandlike solid.[1] This compound can be classified in the group of benzyl halides[2] and has a molecular weight of 175.052 g/mol.[3] This compound has a boiling point of 250–255 °C[3][2] and a melting point of 34–37 °C.[3][2] Xylylene dichloride is used as a vulcanizing agent to harden rubbers. It catalyzes the crosslinking of phenolic resins.[2]
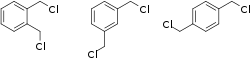 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-xylylene dichloride | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 2928, 2811 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8Cl2 | |
| Molar mass | 175.05 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.202 |
| Melting point | 34–37 °C (93–99 °F; 307–310 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |     |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H302, H314, H315, H317, H319, H330, H400, H410 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P284, P301+312, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P320, P321, P330, P332+313, P333+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P391 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Structure and reactivity
The structure of xylylene dichloride is characterized by an benzene ring with two chloromethyl groups and four hydrogen atoms bound to it.[4] The chloromethyl groups can be located on different sites on the ring, leading to a few different possible forms. These forms are:[3]
- o-xylylene dichloride: 1,2-bis(chloromethyl)benzene
- m-xylylene dichloride: 1,3-bis(chloromethyl)benzene
- p-xylylene dichloride: 1,4-bis(chloromethyl)benzene
The reactive groups of xylylene dichloride are the aryl halides, these are the Cl atoms that are bound to the benzene ring in the side chain. The Cl atoms replace the hydrogen atoms that would usually be located on that site in the ring.[3]
Although the aryl halides are the reactive groups, simple aromatic halogenated organic compounds are very unreactive. With every hydrogen atom that is replaced with a halogen atom, the compound becomes less reactive. This is due to the fact that materials in the halogen group react with strong oxidizers and reducers. Furthermore, they can be react with many amines, nitrides, azo/diazo compounds, alkali metals and epoxides.[3]
Synthesis
Xylylene dichloride can be synthesized from benzenedimethanol. This is done by nucleophilic substitution of the two hydroxyl groups.[5] This reaction occurs with 2HCl.
1, 4-bis(chloromethyl)benzene synthesis technology
Xylylene dichloride can be artificially synthesized with a Chinese invention which relates to a 1,4-bis(chloromethyl)benzene synthesis technology. In this technology, the aromatic hydrocarbon p-xylene and the chemical element chlorine react with an ionic liquid catalyst under LED light source to form a 1,4-bis(chloromethyl)benzene reaction solution. After that, the solution is cooled and separated, so that a crude product is obtained. 1,4-bis(chloromethyl)benzene is obtained by vacuum rectification of the crude product.[6]
References
- Xylylene dichloride. New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services
- "XYLYLENE DICHLORIDE – National Library of Medicine HSDB Database". toxnet.nlm.nih.gov.
- Pubchem. "1,4-Bis(chloromethyl)benzene". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- Blinnikova, Z. K.; Golding, I. R.; Tsyurupa, M. P.; Fomkin, A. A.; Pulin, A. L.; Davankov, V. A. (1 January 2018). "Hypercrosslinked Polycondensation Networks: Copolymers of p-Xylylene Dichloride". Polymer Science, Series B. 60 (1): 91–98. doi:10.1134/S1560090418010013.
- "Hydroxyl Group Substitution". Chemistry LibreTexts. 2 October 2013.
- "1, 4-bis(chloromethyl)benzene synthesis technology" (2015) Chinese patent N105384595A