Zanubrutinib
Zanubrutinib, sold under the brand name Brukinsa, is a medication for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Brukinsa |
| Other names | BGB-3111 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a620009 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| PubChem SID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
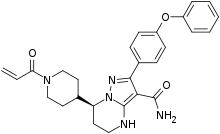
| Formula | C27H29N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 471.5509 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
It was approved for medical use in the United States in November 2019.[3][2][4][5]
Zanubrutinib is classified as a Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor.[6] It is administered orally.[6]
History
Efficacy was evaluated in BGB-3111-206 (NCT03206970), a phase II open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial of 86 patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who received at least one prior therapy.[4] Zanubrutinib was given orally at 160 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.[4] Efficacy was also assessed in BGB-3111-AU-003 (NCT 02343120), a phase I/II, open-label, dose-escalation, global, multicenter, single-arm trial of B‑cell malignancies, including 32 previously treated MCL patients treated with zanubrutinib administered orally at 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily.[4][5]
The primary efficacy outcome measure in both trials was overall response rate (ORR), as assessed by an independent review committee.[4] In trial BGB-3111-206, FDG-PET scans were required and the ORR was 84% (95% CI: 74, 91), with a complete response rate of 59% (95% CI 48, 70) and a median response duration of 19.5 months (95% CI: 16.6, not estimable).[4] In trial BGB-3111-AU-003, FDG-PET scans were not required and the ORR was 84% (95% CI: 67, 95), with a complete response rate of 22% (95% CI: 9, 40) and a median response duration of 18.5 months (95% CI: 12.6, not estimable).[4] Trial 1 was conducted at 13 sites in China, and Trial 2 was conducted at 25 sites in the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, Italy, and South Korea.[5]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted zanubrutinib priority review, accelerated approval, breakthrough therapy designation, and orphan drug designation.[2][4][7]
The FDA approved zanubrutinib in November 2019, and granted the application for Brukinsa to BeiGene USA Inc.[2][4][8]
References
- "Zanubrutinib". DrugBank. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
- "FDA approves therapy to treat patients with relapsed and refractory mantle cell lymphoma supported by clinical trial results showing high response rate of tumor shrinkage". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 14 November 2019. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Drug Approval Package: Brukinsa". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 27 November 2019. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- "FDA grants accelerated approval to zanubrutinib for mantle cell lymphoma". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 15 November 2019. Archived from the original on 28 November 2019. Retrieved 27 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Drug Trials Snapshots Brukinsa". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 14 November 2019. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "BRUKINSA- zanubrutinib capsule, gelatin coated". DailyMed. 18 November 2019. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- "Zanubrutinib Orphan Drug Designation and Approval". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 28 November 2019. Archived from the original on 28 November 2019. Retrieved 27 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Drug Approval Package: Brukinsa". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 27 November 2019. Archived from the original on 28 November 2019. Retrieved 27 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.