12 cm 11th Year Type naval gun
The 12 cm 11th Year Type naval gun was a Japanese naval gun and coast defense gun used on submarines, minesweepers, and torpedo boats of the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II.
| 12 cm 11th Year Type naval gun | |
|---|---|
 A 11th Year Type in a coastal artillery role. | |
| Type | Naval gun Coastal artillery Deck gun |
| Place of origin | Empire of Japan |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1922-1945 |
| Used by | |
| Wars | World War II |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 3,250 kg (7,170 lb) |
| Length | 5.26 m (17 ft 3 in) |
| Barrel length | 4.42 m (14 ft 6 in) |
| Height | 2.1 m (7 ft)[1] |
| Shell | Separate loading 120 x 550R cased charges and projectiles |
| Shell weight | 44 lb 12 oz (20.3 kg) |
| Caliber | 120 mm (4.7 in) |
| Breech | Horizontal sliding-block |
| Recoil | Hydro-pneumatic |
| Carriage | Pedestal mount |
| Elevation | Ship: +10° to +55° Submarine: +10° to +33°[1] |
| Traverse | 360° |
| Rate of fire | 5-6 rounds per minute |
| Muzzle velocity | 2,700 ft/s (820 m/s) |
| Effective firing range | 17,500 yd (16,000 m) at 33°[1] |
Design
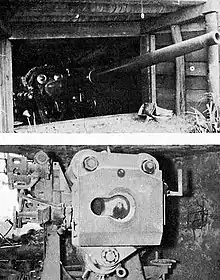
The 12 cm 11th Year Type was a 1922 redesign of the earlier 12 cm/45 3rd Year Type naval gun. The 11th Year Type was a typical built-up gun the period with a central rifled tube surrounded by layers of reinforcing tubes. There may have also been an autofretted mono-block barreled version of the same gun. Estimates on the length of the barrel range between 40 and 45 calibers. The 11th Year Type barrel rested in a ring cradle on a pedestal mount and had a hydro-pneumatic recoil mechanism that consisted of one recoil cylinder below the barrel and two on top.[2] The 11th Year Type differed from the earlier 3rd Year Type because it had a horizontal sliding-block breech and fired separate loading cased charges and projectiles while the earlier gun fired separate loading bagged charges and projectiles. The 11th Year Type was used on smaller naval vessels and submarines possibly because a cased charge was easier to load and wasn't as susceptible to water damage on wet decks. The 11th Year Type had a wider range of elevation and traverse than the 3rd Year Type but with a maximum elevation of +55°, it wasn't really a dual-purpose gun.[2]
Ammunition
| Type | Weight |
|---|---|
| Common Type 0 | 45 lb (20 kg) |
| Common Type 1 | 45 lb (20 kg) |
| Anti-Submarine 1a | 36 lb 5 oz (16.5 kg) |
| Illumination 2a | 45 lb (20 kg)[1] |
Naval Use
Weapons of comparable role, performance and era
- BL 4.7 inch /45 naval gun: British equivalent
- 5"/51 caliber gun: US Navy equivalent
References & External links
- "Tomozuru torpedo boats (1933 - 1934) - Imperial Japanese Navy (Japan)". www.navypedia.org. Retrieved 2019-01-27.
- Campbell, John (1985). Naval Weapons of World War Two. Annapolis, Md.: Naval Institute Press. p. 186. ISBN 0870214594. OCLC 13085151.
- "Otori torpedo boats (1936 - 1937) - Imperial Japanese Navy (Japan)". www.navypedia.org. Retrieved 2019-01-27.
- "KD2 type submarine (I52, 1925) - Imperial Japanese Navy (Japan)". www.navypedia.org. Retrieved 2019-01-27.
- "KD3b type submarines (I56, 1928 - 1930) - Imperial Japanese Navy (Japan)". www.navypedia.org. Retrieved 2019-01-27.
- "Japan 12 cm/45 (4.7") 3rd Year Type and 11th Year Type - NavWeaps". www.navweaps.com. Retrieved 2019-01-27.
- "KD4 type submarines (I61, 1929 - 1930) - Imperial Japanese Navy (Japan)". www.navypedia.org. Retrieved 2019-01-27.
- "5-go minesweepers (1929) - Imperial Japanese Navy (Japan)". www.navypedia.org. Retrieved 2019-01-27.