1812 United States elections
The 1812 United States elections elected the members of the 13th United States Congress. The election took place during the First Party System, and shortly after the start of the War of 1812. The Federalist Party made a relatively strong showing, winning seats in both chambers while supporting a competitive challenge to the incumbent Democratic-Republican President. However, the Democratic-Republican Party continued its control of the Presidency and both houses of Congress.
| Presidential election year | |
| Incumbent president | James Madison (Democratic-Republican) |
|---|---|
| Next Congress | 13th |
| Presidential election | |
| Partisan control | Democratic-Republican hold |
| Electoral vote | |
| James Madison (DR) | 128 |
| DeWitt Clinton (DR/F) | 89 |
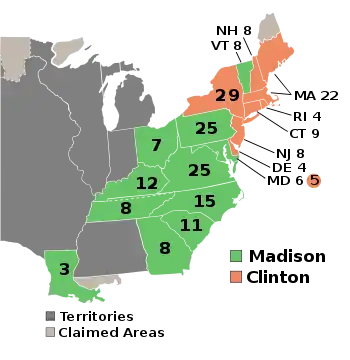 | |
| 1812 presidential election results. Green denotes states won by Madison, burnt orange denotes states won by Clinton. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |
| Senate elections | |
| Overall control | Democratic-Republican hold |
| Seats contested | 12 of 36 seats[1] |
| Net seat change | Federalist +2[2] |
| House elections | |
| Overall control | Democratic-Republican hold |
| Seats contested | All 182 voting members |
| Net seat change | Federalist +32[2] |
In the Presidential election, incumbent Democratic-Republican President James Madison defeated New York Lieutenant Governor and New York City Mayor DeWitt Clinton.[3] Clinton was a member of the Democratic-Republican Party, but his presidential bid received the support of both anti-Madison Democratic-Republicans and many Federalists.[4] Although Madison won, the Presidential election was the closest since the 1800 election, as Clinton won New England and three mid-Atlantic states.
Following the 1810 census, 39 seats were added to the House. Federalists won major gains, but Democratic-Republicans continued to dominate the chamber.[5]
In the Senate, Federalists picked up a small number of seats, but Democratic-Republicans retained a dominant majority.[6]
See also
References
- Not counting special elections.
- Congressional seat gain figures only reflect the results of the regularly-scheduled elections, and do not take special elections into account.
- "1812 Presidential Election". The American Presidency Project. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
- History of American Presidential Elections, Volume I 1789-1844; Arthur M. Schlesinger Jr.; Pgs 249-272
- "Party Divisions of the House of Representatives". United States House of Representatives. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
- "Party Division in the Senate, 1789-Present". United States Senate. Retrieved 25 June 2014.